General requirements for drawing up a business plan. Requirements for a business plan. Marketing, organizational and production plan
It is known that an enterprise in a market economic system is subject to constant, largely contradictory changes and influences. In addition to this for Russian conditions The instability of legislation is also characteristic. Such conditions external environment the existence of the company leads to thoughts that boil down to the simplest phrase: “Maybe it’s not worth spending time and effort on drawing up a plan, but it’s better to constantly be sensitive to changes and keep the steering wheel in a position of immediate readiness for them?”
Market experts believe that the larger the market, the more important the plan. At the same time, the plan must be understood as a set of measures balanced with resources, taking into account the risks of loss of funds that arise in the new conditions and the very limited influence of the state on the rules of a market economy.
Developing a business plan requires professional knowledge in the field of management, finance, and marketing. Therefore, even small firms in the West turn to experts for advice or to specialists offering services for drawing up a business plan.
However, drawing up a business plan requires the personal participation of the manager or entrepreneur opening his own business. The leadership role of the first person in the business planning process necessitates his participation in modeling future activities, balancing his strengths, the resources of the enterprise, the possibility of attracting additional funds and their efficient use. The personal participation of the manager in drawing up the business plan is so important that many foreign banks and investment firms refuse to consider applications for funds at all if it becomes known that the business plan was prepared from start to finish by an outside consultant and was only signed by the manager.
By getting involved in this work personally, the leader, as it were, models his future activities, checking both the plan itself and himself - will he have enough strength to bring it to success and move on? This does not mean, of course, that there is no need to use the services of consultants - on the contrary, the involvement of experts is highly welcomed by investors. 1
No legal document yet stipulates the obligation to prepare a business plan. Even banks do not always require it when providing loans. But neglecting to draw up a business plan, the entrepreneur turns out to be unprepared for the troubles awaiting him and usually begins to feverishly improvise. And this most often ends in failure. Therefore, it is better not to waste time (despite the fact that for a large project the development of a business plan can last up to 200 hours or more) and engage in business planning, the benefits of which are confirmed by foreign experience.
Mastering the art of writing a business plan in an environment Russian economy has become extremely relevant due to the following reasons:
Firstly, a generation of entrepreneurs is being born in our economy who do not yet have experience in managing in market conditions;
Second, changing economic conditions require experienced managers to pose and solve problems in new ways;
Thirdly, to attract foreign investment You must be able to substantiate your applications and prove your abilities and capabilities to investors.
A business plan is a comprehensive description of the business and the environment in which it operates, as well as the management system it needs to achieve its goals.
There is no standard for developing a business plan due to the diversity of business goals and the endless variations in the environment in which it operates. Consequently, it takes skill and perseverance to describe a three- or five-year business outlook, especially in Russia's rapidly changing economic environment. Therefore, a significant part of any business plan will be sections on systematic control and regulation of business. While a business plan is generally considered a tool for obtaining credit, it serves other purposes as well.
A business plan is an analytical document for planning entrepreneurial activity, it describes all the main aspects of the future commercial enterprise, all the problems that it may encounter are analyzed, and ways to solve these problems are determined. A properly drawn up business plan ultimately answers the question: is it worth investing in this business at all and will it bring profit? It is very important to draw up a business plan in accordance with certain requirements and perform special calculations - this will help to anticipate future problems and understand whether they are surmountable and where to “lay straws” in advance.
The importance of planning should not be underestimated. A sober look at
an enterprise being created or an already created one will help identify its strengths and weaknesses; determine exactly what is required; not to lose sight of anything; assess the emerging prospects and begin to develop a plan of specific actions aimed at achieving the goal; foresee possible difficulties, to prevent them from developing into a serious problem, to get to the bottom of the causes and difficulties, and, therefore, to find ways to eliminate them.
If the business being started is on the verge of bankruptcy, the plan will explain why it is cheaper to abandon the dubious venture than to learn from personal experience what the plan would have taught during several hours of concentrated work on its preparation. A carefully crafted business plan can be quickly developed into a business proposal or financial application that is sure to satisfy lenders.
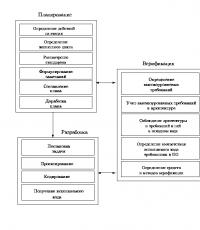
The organization of drawing up a business plan can be represented by the following diagram:
1. Making a decision to create your own business or implement a new commercial project.
2. Analysis of one’s own capabilities and ability to take on the implementation of the planned project.
3. Selection of a product or service, the production (provision) of which will be the goal of the project.
4. Research possible market sales
5. Drawing up a forecast of sales volumes (for the first year - monthly, for the second - quarterly).
6. Selecting a location for commercial and/or production activities.
7. Development of a production plan.
8. Development of a marketing plan.
9. Development of an organizational plan.
10. Development of a legal scheme for future commercial activities.
11. Solving issues related to the organization of accounting.
12. Solving insurance issues.
13. Development of a financial plan.
14. Writing a summary for a business plan.
2.2. Business plan structure.
It should be noted that different economists identify slightly different structures of business plans, but they all have approximately the same structure.
A business concept (resume) is a concise, quickly readable overview of information about the planned business and the goals that the enterprise sets for itself when starting a business or developing an existing one.
In essence, the concept is a shortened version of the business plan itself.
The resume should reflect the following main points:
business opportunities;
business attractiveness;
importance for the enterprise and the region;
necessary financial resources (own or borrowed);
project payback period;
possible period for repayment of borrowed funds;
investment conditions;
expected profit and its distribution
The order in which the concept is presented is quite free, but it must begin with the main goal of the proposed business (usually making a profit) and the purpose of the business plan being developed.
The business concept (resume) is drawn up at the end of writing a business plan, but is at the beginning.
The section describing the current situation and providing brief information about the enterprise reflects the following points:
the main events that influenced the emergence of ideas for the business plan;
the main circumstances and problems facing managers;
market condition and position to be achieved
In the section characterizing the business object, it is necessary to note the focus of the business plan (products, works, services, creation of a new enterprise, development of an existing one, financial recovery). It is also necessary to note here the importance of the product for consumers, its uniqueness. It is also advisable to characterize functionality and product features.
The section ends with a description of the key factors that should determine the success of the proposed business.
Research and market analysis are aimed at identifying today's consumers of products and services and identifying potential ones. In this section, it is desirable to determine the priorities that guide the consumer when purchasing: quality, price, time and accuracy of delivery, service maintenance and so on.
It is necessary to segment the market, determine the size and capacity of markets for the company’s products.
It is necessary to analyze how quickly products and services will establish themselves in the market and justify the possibilities of its further expansion, as well as the main factors influencing this.
Monitoring and evaluating competitors is also very important. It is necessary to identify and analyze their strengths and weaknesses.
It is necessary to determine the possible sales volume in physical and monetary terms.
Financing
These requirements have been prepared by FORMAP based on methodological recommendations Federal Fund for the Support of Small Business of the Russian Federation in order to assist small businesses in drawing up a business plan.
A business plan is both a tool for attracting investment and the basis for intra-company planning. The sequence of drawing up and principles of detailing a business plan for different companies and projects do not coincide. When drawing up a business plan, it is necessary to take into account that this is always an iterative process, which involves making changes based on newly received information and the application of different scenarios. At the same time, there is an internal logic to the structure of the business plan and its generally accepted developments.
The recommended structure of a business plan with brief recommendations for its development is not mandatory; FORMAP will consider business plans written in another form (provided all key issues are covered). The form in which the business plan is presented will largely depend on the issues that are most significant for the enterprise and the need to raise funds foreign companies, funds and other creditors; in the latter case, compliance with generally accepted requirements in international business practice is required.
Following the requirements of the scenario approach, it makes sense to develop several alternative forecasts of changes in the value of the initial data, corresponding to pessimistic and optimistic options for the development of the project.
It is recommended to draw up the financial part of business plans using the Project Expert software product of the PROINVEST CONSULTING company, or the Alt-Invest packages of the Alt company, ANALYTIC of the INEC company. (It should be noted that the mere use of these or other software products does not yet guarantee the preparation of a business plan at a high-quality level, and FORMAP reserves the right to request additional information or insist on finalizing the submitted documents).
2. Description of the enterprise
2.1. Goals and objectives for the immediate period and future.
2.2. The history of the company's creation, a list of main owners, the role of each of them in the founding and activities of enterprises.
2.3. Events that influenced the development of the enterprise.
2.4. Analysis of strengths and weaknesses enterprises:
Technology level;
Use of know-how;
Quality of products and services;
Level of production costs and their analysis;
Terms of supply of materials and components;
Geographical location of the enterprise;
Nearest transport routes;
Geographical location of clients;
What problems does the company face?
Main competitors and their strengths;
What are the advantages of the company compared to competitors.
2.5. Organizational structure And personnel composition:
Experience and qualifications of personnel;
Assessment of management level.
2.6. Main achievements of the enterprise:
Enterprise performance indicators for the last 3 years;
What customer needs does the company provide?
The volume of products or services provided by the enterprise;
The company’s market share and what are the trends towards its change.
3. Description of products (services)
This section provides detailed characteristics of the products or services produced by the enterprise, compares them with the products of competitors, and analyzes production development plans.
3.1. Product characteristics:
Functional purpose of the product, for what purpose it is intended;
Examples of product use;
Cost depending on production volumes;
Manufacturability;
Versatility;
Product compliance with accepted standards;
What stage is the product currently at (idea, working draft, prototype, mass production, etc.);
Quality control requirements;
User training requirements;
Requirements for warranty and post-warranty service;
Are there opportunities for further development of the product;
Patent and licensing protection;
The main qualities of this product (design, packaging, etc.);
A visual representation of the product (photo or drawing).
3.2. Analysis of competitors' products available on the market:
Analogs that can replace the product planned for release on the sales market;
Description of the functional and consumer properties of competing products;
Why competitors’ products are in certain demand;
Pricing principles of competitors;
Sales promotion methods used by competitors.
3.3. Research and development:
Goals and description of planned R&D;
Existing technological risks;
The technological state of competitors, the possibility of their technological achievements to influence or influence the activities of the enterprise in the future;
Description of the product development concept for the next generations.
3.4. Conditions for purchasing raw materials, materials and components:
List of the main raw materials used to produce the new product;
Description of the main suppliers;
Current state of relations with suppliers (existence of contracts, agreements, etc.);
Location of suppliers;
The degree of novelty of the supplied components for the production of this product and their share in the supplier’s products;
Terms of payments and deliveries (credit, prepayment, advances, etc.);
Delivery times;
Inventory level;
Industrial cooperation.
5. Organizational plan
This section should analyze the immediate organization of work, including the launch of production and the work plan for the first year.
The organizational plan must be consistent with the company's marketing plan.
In addition, the following should be described:
Organizational structure of the project implementation;
Project implementation schedule;
Management team and leading specialists;
Future management structure of the company.
6. Production plan
This section should describe in detail the way in which the enterprise plans to efficiently produce products or services and deliver them to the customer.
6.1. Description technological process:
The need and conditions for the acquisition of technological and other equipment;
The need for land, buildings and structures, communications;
The need and conditions for the supply of raw materials, materials, components, production services, quality control and supply discipline;
Requirements for energy sources and their availability;
Technology production process in the form of a diagram;
Requirements for preparation of production;
Opportunities for improving production technology;
Requirements for quality control at all stages of production;
Information about the accounting system at the enterprise;
6.2. Qualification requirements and availability necessary personnel:
Structure and composition of divisions;
Administrative staff;
Engineering and technical personnel;
Terms of payment and incentives;
Working conditions;
Training;
Anticipated changes in the personnel structure as the enterprise develops.
7. Sales plan
The sales plan should reflect the company's sales strategy in various time periods.
7.1. Company sales strategy:
Accepted pricing concept;
Pricing trend for a certain period (six months, a year, a number of years). Indicate the main reasons that could affect changes in prices for the product planned for release;
The price of the product at which it is possible to obtain optimal profit (planned markup including VAT);
The price level to which consumers are accustomed for a given product and in a given market. The percentage difference in prices for a given product with prices for a similar product from competing companies;
The ability of the established price for a given product to maintain (expand) the company’s participation in the market;
Product sales scheme (with advance payment, on credit, for export);
Optimal order sizes and forms of payment;
Terms of payment (in fact, with prepayment, on credit);
Discount amounts;
Sales time;
Inventory level;
Loss percentage.
This section of the business plan should provide an opportunity to assess the project's ability to generate revenue. Money in an amount sufficient to service the debt (or pay dividends when we're talking about on investments), the conditions for attracting investments, guarantees provided to the investor for the return of funds must be described.
The need for financial resources, proposed sources and schemes of financing, borrower responsibility and guarantee system. Particular importance should be given to describing the current and projected state of the environment. economic environment. Factors that are difficult to predict and their alternative values for various scenarios should be reflected.
A clear breakdown of project costs and use of funds, especially the use of FORMAP funds, is required.
The conditions of all other loans related to the project or already on the balance sheet must be described.
It is necessary to clearly show how and by whom (the enterprise itself or an independent contractor) the cost estimate was prepared; the expected degree of clarity of the estimate.
The conditions, estimates and assumptions on the basis of which the calculations are made must be described. financial results project.
It is necessary to reflect (monthly, quarterly, yearly):
Changes in the ruble to dollar exchange rate;
List and rates of taxes;
Ruble inflation (various % depending on the object);
Capital formation through own funds, equity issue loans, etc.
The procedure for repaying loans, interest on them, etc.;
How, in the opinion of the enterprise, will FORMAP be able to withdraw capital if it or the enterprise is not interested in FORMAP's participation in the share capital on an ongoing basis.
Usually financial section The business plan is represented by at least three main documents:
Profit and loss statement (shows the operating activities of the enterprise by period);
Cash flow plan (Cash Flow).
Balance sheet ( financial condition enterprises at a certain point in time);
If necessary, a loan repayment and interest payment schedule can be provided; information about working capital indicating changes and initial assumptions during the loan; expected tax payment schedule.
In addition, calculations of the main indicators of solvency and liquidity, as well as projected project performance indicators, are attached.
The timing of the forecasts must coincide (at a minimum) with the timing of the loan/investment that is requested for the project.
9. Project sensitivity analysis
It is necessary to analyze the sustainability of the project to possible changes both the economic situation as a whole (changes in the structure of taxes, inflation rates, etc.) and internal indicators of the project (changes in sales volumes, product prices, increase in payment delays, etc.).
10. Environmental aspects of the project
A description of the national, regional, and local protection requirements that apply to the project should be provided. environment, protecting personnel health and ensuring safety regulations.
Location of project facilities;
Use of land allocated for the facility in the past and present;
Description construction work or physical changes, territories by the project;
Proposed measures to mitigate or improve environmental impacts;
Statement on the distribution of responsibilities for any contamination and/or/ responsibility for it;
Amounts of fines for environmental pollution;
Any statements by the enterprise about its environmental policy.
11. Normative base project implementation:
Government licenses or permits required to carry out the project; how the company intends to obtain them and how long it will take;
The nature of tariffs and quotas for the import of raw materials, materials and components;
Presence of restrictions on imports in sales markets abroad.
12. Social significance of the project
Economic and social benefits from this project for the territory, region, country.
Applications
Attachments include documents that can serve as confirmation or further explanation of the information presented in the business plan. The mandatory ones include the following:
Biographies of enterprise or project managers confirming their competence and work experience;
results marketing research;
Auditors' reports (including the analytical part);
Detailed specifications products;
Letters of guarantee or contracts with suppliers and consumers of products;
Lease, rental, licensing agreements;
Conclusions of state supervision services on environmental and safety issues, sanitary and epidemiological services;
Articles from magazines and newspapers about the activities of the enterprise;
It is also possible to provide as an annex to the business plan:
Photos or videos of product samples;
Enterprise plan;
The economic essence of a business plan is to introduce a potential investor (business partner, bank, etc.) to the essence of the proposed project and interest him in participating in this project. In order for this document to be adequately perceived by potential project participants and to serve as a basis for them to make informed business decisions, it must meet a number of criteria.
The business plan must contain all the necessary sections in order to reflect the investment project under consideration as fully as possible. This means that the business plan must contain all the information that a potential investor or business partner may need to make a positive decision. In addition, the completeness of the presentation of the project in the business plan means that this document must cover a period of time sufficient to complete the described project or to reach the planned level of production, sales, construction, etc.
Utility
The information presented in a business plan should not only be complete, but also useful. You should not include in the business plan something that you can do without and that will not in any way affect the potential investor (business partner) making a positive decision. For example, information about average number employees of the enterprise - the initiator of the project can be useful and interesting. However detailed description the social structure of the personnel (the number of working men and women, the presence of employees with higher or secondary education, the designation of people whose work experience exceeds five years, etc.) may be unnecessary. Another example: if the implementation of a project requires the enterprise to have certain licenses, then a list of them indicating the validity period of each license must be included in the business plan. At the same time, a detailed consideration of legislative and regulatory acts regulating this type activities, it is recommended to leave them “behind the scenes” (you can briefly list these documents, indicating their date, number and name of the body that issued the document).
Neutrality
Reality and authenticity
A business plan must be drawn up on the basis of information that can be assessed as reliable. Deliberate distortion of project parameters in order to improve its attractiveness is not allowed.
All conclusions and proposals contained in the business plan must be based on real and reasonable evidence, supported by specific facts and examples. In addition, there should be an analogy between the data presented in the business plan and the current state of affairs (or the current market trend). All more or less significant discrepancies should be commented on reasonably, otherwise the business plan will look adventurous, which will most likely cause a negative reaction from a potential investor (business partner).
Transparency
The business plan should be written consistently and logically so that any user can trace the rationale for the project parameters and business plan conclusions.
Flexibility
The business plan should be written with the possibility of adjusting it with the least amount of effort. The need for changes arises when deviations occur during the implementation of the project and aims to change the project parameters in such a way as to ensure the maximum possible effect under new conditions.
Controllability
A business plan must be a reliable and reliable control tool, that is, it must, using a system of specific indicators, allow one to monitor compliance with work deadlines, production (construction) volumes, supplies and sales, as well as the compliance of actual indicators with planned data.
Understandability
One of the most essential requirements for a business plan is that it is written in an accessible, in clear language, in compliance with accepted terminology and clear, unambiguous formulations. A potential investor or business partner should not and will not delve into obscure and vague definitions, understand unclear indicators and study unnecessary conclusions.
Compact and structured
The optimal volume of a standard business plan is no more than 50-80 printed sheets of A4 format. As practice shows, this volume contains all the necessary information. The requirements for a business plan include all the really necessary information about even the most complex and large investment project. Significantly exceeding the sufficient volume of a business plan makes it extremely difficult for potential investors to perceive it. In addition to the business plan, it is also useful to create a short presentation of 10-20 slides, which contains the most important organizational, technical and financial parameters of the project. All information presented in the business plan should be grouped into sections, excluding ambiguities of interpretation and repetitions. In this case, the main text of the business plan should contain only information related to the essence of the project. All voluminous elements of the document (accounting and financial statements, research results, etc.) should be presented in the form of appendices and located at the end of the document.
Visibility
In many cases, a verbal description of a project is not as effective and understandable as a graphical representation. For example, it is much easier and more convenient to describe the dynamics of changes in any indicators not with words, but with the use of diagrams. This way, a potential investor spends less time getting acquainted with projects with minimal costs, greater pleasure and a better understanding of the essence of the document. These are the basic requirements that every competently and professionally drawn up business plan must meet, the purpose of which is to interest investors and serve as a real tool for implementation and control investment project. Let's look at the typical structure of a standard business plan.
Typical business plan structure
The structure of a business plan is a certain logical sequence of its sections, ensuring the most complete and clear presentation of the investment project in order to accept it management decisions. In most cases, the structure of a standard business plan should include the following sections: summary; introduction;
The summary is the first information about the project that a potential investor will see. The main purpose of the resume is to interest the investor, making him want to read other sections of the business plan. A resume is a “business plan in miniature”, it contains in a concentrated form all the information about the project disclosed
Despite the fact that this section is the first, it is written last. This is not difficult to do: you need to go through all sections of the business plan and take one or two of the most significant conclusions from each. After reading the summary, the investor should receive the following information.
Summary.
The resume is written last, after the business plan as a whole has been drawn up. It should include the main provisions and ideas of the business plan, the conclusions to which the entrepreneur came.
Resume structure should consist of 3 parts:
Introduction: includes the goals of the plan, a briefly expressed essence of the project;
main content: a concise summary of all the key elements of the business plan and its main parts: type of activity, demand forecast, sources of financing, etc.;
conclusion: summarizes the factors for the future success of the entrepreneur, may include a description of the main methods of action of the entrepreneur.
Having the right idea about your resume is extremely important for writing a resume. The resume should be short, usually three to four pages, but it is better if the resume fits on one page. The executive summary is the key part of the document that “sells” it to the investor, and it should be written in such a way that the reader will want to continue reading the business plan. That is, the resume should attract not by quantity, but by quality, taking into account the specifics of the activity and the requests of potential investors.
Essence of the project
First of all, the investor is presented with information about the project with which he is dealing. The essence of the project could be the construction of a cottage village, the organization of production of a new bus model. replacement of existing equipment in order to save energy costs, etc.
Initiator of the project
The name of the project initiator is given, the experience of implementing similar projects and the stability of the financial condition are assessed.
Project competitiveness factors
This paragraph of the summary is perhaps the most significant. He must convince the investor that the planned project has every chance of being successfully implemented, and that the results of its implementation are in demand by the market. No other source of return on the investor’s investment than effective sales on the market, the project does not. Consideration of the main factors listed in the summary that ensure the competitiveness of the project's products allows the investor to assess the compliance of the characteristics of the project's products with existing and future market trends and, as a result, determine how likely it is that the sales planned by the project will take place. Here are some examples of presenting competitiveness factors in a resume.
Project financing
In addition to the essence of the proposed project and the factors ensuring its success, the investor needs to know from what sources the financing is planned and how much money he should personally invest to participate in this project. The summary briefly describes how much money will be invested by each of the potential investors in the project: their own or borrowed funds. If a loan is attracted to the project, then it is necessary to indicate not only its amount, but also the total loan period and the annual interest rate.
Economic results of the project
The economic results of the project imply the following indicators: the amount of revenue (for the year and for the entire horizon of the project); the amount of net profit (on average for the year and for the horizon of the project); sales profitability, defined as the ratio of net profit to revenue (annual average).
If you want to start own business, but you don’t have enough money, then you can’t do without such a document as a business plan. This document is provided to the prospective investor as a guarantee that his money will certainly be repaid and will not be thrown down the drain.
Classification of business plans
Business plans can be different. Here you can get acquainted with their structure in more detail. They are usually divided according to the following criteria:
- By type - depending on the field of activity that the project is focused on. There are organizational, technical, social, economic and mixed business plans;
- By class - depending on the composition, structure and subject area. There are mono- (a separate project), multi- (a project consisting of several mono-projects), mega-business plan (a program for the development of an industry, region, etc., which consists of many mono- and multi-business plans;
- By scale - depending on the size of the project, the number of participants in it and the extent of its impact on the world around us. There are very large, large, medium and small projects. In addition, the division can be by region - interstate, international, national, interregional, regional, intersectoral, sectoral, corporate, departmental, intra-enterprise projects;
- By duration - depending on the duration of the time period within which the project will be implemented. There are long-term (the implementation of which must take more than 5 years), medium-term (3-5 years) and short-term projects;
- By complexity - different aspects of complexity are calculated (for example, financial, technical, etc.). There are very complex, complex and simple business projects;
- By type - depending on the nature of the subject area of the project. There are organizational, innovative, research, teaching and mixed projects.
You can read more about the types of business plans.
Requirements for writing a business plan

Mastering the art of writing a business plan is one of the necessary qualities for modern successful person. So for successful project You will have to comply with certain requirements for the business plan:
Greeted by clothes
The business plan should be attractive, but discreet. Remember: this document will be the first thing the investor sees and learns about your project. It will create an image that will follow you for a long time.
More details

The more substantive details a document contains, the more trust it will generate. However, it is better not to overdo it. Make sure that the main principles of the document are brevity, clarity, and a clear structure for presenting information.
According to foreign studies, it has been proven that the ideal length of a business plan is 40 pages. But in some cases it makes sense to write out the plan in more detail - up to 70-80 pages. And vice versa - if necessary, you can reduce the volume of the document to 30 pages or even less.
Only important
No background or secondary information - only the most important things. If you want, you can include additional information in the appendices - they will help increase the flexibility of the project and satisfy the interest of pedantic investors.
On a note! A large number of important information is best presented in a table, chart, chart, or other graphical or analytical form. When it is necessary to compare and analyze, this form of presenting information will contribute to its better assimilation, and therefore brings more results.
We pay attention to style
Write as much as possible in simple language, do not use too many terms - do not use anything that may impede understanding, serve as a barrier to the perception of the information you want to convey.
Your business plan should be understandable not only to investors, but also to as many people as possible. Try to be convincing, concise, and arouse interest.
Be honest with everyone

It is necessary to objectively assess all the difficulties that stand or may stand in the way of implementing the business plan. This document is a project to solve such difficulties.
However, all your assumptions and forecasts must be supported by facts, research, statistics, and expert opinions.
If the plan is unrealistic, few investors will want to work with you. A clear understanding of the risks and how to overcome them will show creditors how prepared you are to manage the company and achieve your goals.
By the way! For our readers there is now a 10% discount on any type of work, even writing a business plan
Summary
Often investors prefer to read briefly about what is contained in the document before getting acquainted with the project itself. Experienced lenders already from brief description they see whether the project is worthwhile or not, they will notice all its strengths and weaknesses.
Investors also pay attention to the completeness of the answer to 4 vital questions for the project: management team, current and expected in the future financial indicators, goods and services, marketing plan. So it is vital to prepare a strong argument for each of these points.
Here you can see examples of a business plan for a gas station and a sports bar:
The basic procedure for drawing up a business plan may vary. We bring to your attention the most popular option:
- Summary,
- Company,
- Product/service,
- Sales market,
- Competition,
- Marketing,
- Production,
- Organization, management, personnel,
- Finance,
- Risk assessment and insurance.
There are other factors that will determine the composition, volume, structure, and degree of detail of the business plan:
- Specifics of the type of business activity;
- Size of the organization;
- Purpose of the business plan;
- General strategy of the organization;
- Growth prospects;
- The volume of the expected sales market;
- Presence of competition.
On a note! A business plan can be not only the initial document from which the entire enterprise starts, but can also become the internal law of the company.
In general, you already understand that this document is quite serious. And if you want your idea to be crowned with success, if you want lenders and investors to be interested in your project, then devote yourself completely to this document. Well, if you are burdened with studying at this time, our specialists will be happy to help.
In the context of the transition to a market economy, mastering the art of drawing up a business plan becomes extremely important. Western investors are wary of dealing with Russian entrepreneurs. And not only because of the lack of guarantees, the instability of the economic and political situation in the country, as is commonly believed, but also because of unprofessional, unconvincingly developed documents, in particular business plans.
We list a number of general requirements that must be taken into account when preparing a business plan:
- - a business plan is the first thing a potential investor learns about a company, so it is necessary that the design of the business plan corresponds to the image of a successful company: it should be attractive, but discreet;
- - the degree of detail should correspond to the goals of the plan, but not include anything superfluous: a clear structure of the material and its clarity, brevity. Foreign practice shows that the optimal (standard) volume of a business plan is 40 pages. However, in some cases more detailed business plans of up to 70-80 pages are required. If, to ensure completeness and specificity of the presentation required material the business plan requires less volume, then the number of pages of the business plan can be reduced to 30 pages or less;
- - the business plan should not include secondary and reference Information. It is better to put it in applications. Typically, investors request additional information, and the presence of applications increases the flexibility of the project. The volume of applications is not limited;
- - presentation style: simplicity of presentation and absence of language and terminological barriers, i.e. accessibility to study and understanding;
- - a business plan should be understandable to a wide range of people, and not just specialists. It should also be convincing, concise, and arouse interest among partners.
- - attention should be paid to the dual nature of the business plan. On the one hand, this is a serious analytical document, and on the other, an advertising medium;
- - reasonable dosage when presenting the technology of a business proposal;
- - when drawing up a business plan, you must also remember that the information presented in it must be succinct, clear and at the same time concise. In this regard, it is recommended to use the method of collapsing information: it is classified into certain categories (indicators) and presented in analytical (tabular) or graphical form. In a systematic form, when possible comparative assessment, digital data is perceived much easier, and therefore more effective;
- - an objective assessment of the difficulties standing in the way of implementing what is planned in the business plan;
- - the business plan must be honest analysis, based on realistic assumptions. Assumptions and forecasts must be substantiated and supported by references to sources of information, such as market research (surveys), industry statistics, economic and demographic studies, as well as opinions of persons who will do business with the company. Few investors or lenders will take risks based on unrealistic plans. A business plan shows investors and creditors the quality and depth of a company's leadership and notes managerial ability achieve your goals;
- - accuracy of financial calculations;
- - the company's risks should be discussed. Trust in the company can be seriously undermined if existing risks and problems are disclosed not independently, but from the outside;
- - Do not make irrelevant or vague statements. For example, statements such as “sales will double in next year” or “a product line will be introduced” should be deleted and detailed explanations provided. Claims must be specific and supported by marketing information and other data;
- - the plan must be comprehensive and include a discussion of the organizational strategy for achieving the company's advantages and overcoming potential difficulties;
- - many investors like to read one or two pages summary business plan (summary), which allows them to see the important features and benefits of the project. There are also four vital important block key issues addressed in the business plan, which are especially carefully assessed by investors: management team, current and planned financial indicators, goods and services, marketing plan. It is necessary to prepare a strong argument in each of these sections;
- - the business plan must be prepared taking into account the requirements and standards of organizations and individuals to whom this document is intended to be presented;
- - the business plan must be presented in an attractive, and not overly complex, form and reproduced in a sufficient number of copies for its consideration.
It should be remembered that in general, business planning is a very labor-intensive and rather lengthy process. An entrepreneur has to spend weeks and months creating a business plan. Various business planners agree that the total time required for this is about 200 hours.