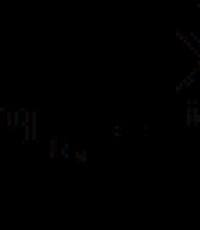Ability to find organizational and management solutions. Organization and control of the implementation of management decisions. Target and processor technologies
In the process of economic and financial activities of organizations, situations constantly arise when there is a need to choose one of several possible options for action. As a result of such a choice, a certain solution appears.
In order to correctly determine the effectiveness management decisions, it is necessary to carry out separate accounting of income and expenses trade organization in the context of individual product groups. However, in practice, maintaining such records is very difficult. As a result, it is advisable to use the so-called specific quality indicators in the analysis, namely profit per 1 million rubles of turnover, as well as distribution costs per 1 million rubles of inventory.
The effectiveness of management decisions in a trade organization is manifested in a generalized way in quantitative form as an increase in the volume of trade turnover, acceleration of the turnover of goods, and a decrease in the amount of inventory.
The final financial and economic result of the execution of management decisions is manifested in an increase in the income of a trading organization and in a reduction in its expenses.
Economic efficiencyDefinition economic efficiency management decisions, as a result of which the execution increased, and, therefore, increased, can be carried out using the following formula:
Eph = P*T = P * (Tf - Tpl),
- Eph— economic efficiency (in thousand rubles);
- P— profit per 1 million rubles of trade turnover (in thousand rubles);
- T— increase in trade turnover (in million rubles);
- Tf- actual trade turnover that takes place after the implementation of this management decision;
- Tpl— planned turnover (or turnover for a comparable period before the implementation of this management decision).
In the example under consideration, the economic efficiency of making and executing a management decision is expressed in a reduction in the amount (selling expenses, or commercial expenses) attributable to the balance of goods. This leads to an increase in the amount of profit received. This efficiency can be determined by the following formula:
Ef =IO*Z = IO*(Z 2 - Z 1),
- Eph— economic efficiency of this management activity (in thousand rubles);
- AND ABOUT— the amount of distribution costs per 1 million rubles of inventory (in thousand rubles);
- 3 — amount of change (decrease) in inventory (millions, rubles);
- 3 1 — the amount of inventory before the implementation of a management decision (event) (million rubles);
- 3 2 — the amount of inventory of goods after the implementation of this management decision.
In addition, the economic efficiency of the implemented management decision affected the acceleration of commodity turnover. This influence can be determined by the following formula:
Eph = Io*Ob = Io (Ob f - Ob pl),
- Eph— economic efficiency of management decisions (thousand rubles);
- And about— simultaneous value of distribution costs (thousand rubles);
- About— acceleration of goods turnover (in days);
- About pl— turnover of goods before the implementation of a management decision (in days).
- About f— turnover of goods after the implementation of a management decision (in days).
Methods for analyzing management decisions
Let's consider the procedure for applying the basic methods and techniques of analysis when assessing the effectiveness of making and executing management decisions.
Comparison method makes it possible to evaluate the activities of the organization, identify deviations of the actual values of indicators from the basic values, establish the reasons for these deviations and find reserves for further improvement of the organization’s activities.
Index method used in the analysis of complex phenomena, the individual elements of which cannot be measured. As relative indicators, they are necessary to assess the degree of fulfillment of planned tasks, as well as to determine various phenomena and processes.
This method makes it possible to decompose the general indicator into deviation factors.
Balance sheet method consists in comparing interrelated indicators of an organization’s performance to identify the influence of individual factors, as well as to find reserves for improving the organization’s performance. In this case, the relationship between individual indicators is expressed in the form of equality of results obtained as a result of certain comparisons.
Elimination method, which is a generalization of the methods of index, balance sheet and chain substitutions, makes it possible to isolate the influence of a single factor on a general indicator of an organization’s performance, based on the assumption that the remaining factors acted under other equal conditions, i.e. just as planned.
Graphical method is a way to visually illustrate the activities of an organization, as well as a way to determine a number of indicators and a way to present the results of the analysis.
Functional cost analysis(FSA) is a systematic research method used in accordance with the purpose of the object being studied (processes, products) in order to increase the beneficial effect, that is, the return per unit of total costs for the life cycle of the object.
The most important feature of functional cost analysis is to establish the feasibility of a list of functions that the designed object must perform under certain specific conditions, or to check the necessity of the functions of an existing object.
Economic and mathematical methods of analysis are used to select optimal options that determine management decisions in existing or planned economic conditions.
Using economic and mathematical methods of analysis, the following problems can be solved:- assessment of the production plan developed using economic and mathematical methods;
- optimization production program, its distribution between workshops and individual types of equipment;
- optimization of the distribution of available production resources, cutting of materials, as well as optimization of norms and standards for reserves and consumption of these resources;
- optimization of the level of unification of individual component parts of the product, as well as technological equipment;
- determining the optimal size of the organization as a whole, as well as individual workshops and production areas;
- establishing the optimal range of products;
- determination of the most rational routes for in-plant transport;
- determination of the most rational periods for the operation of equipment and its repairs;
- comparative analysis of the economic efficiency of using a unit of a type of resource from the point of view optimal option management decision;
- determination of possible intra-production losses in connection with the adoption and implementation of the optimal decision.
Let's summarize this chapter. The effectiveness of an organization's functioning depends to a very large extent on the quality of management decisions. This makes it important for all responsible employees of the management apparatus, and above all heads of organizations, to acquire theoretical knowledge and practical skills in the development and implementation of optimal management decisions.
Development and adoption of management decisions- this is usually a choice of one of several alternative options. The need to make management decisions is determined by the conscious and purposeful nature of human activity. This need arises at all stages of the management process and forms part of any management function.
The nature of management decisions made is greatly influenced by the completeness and reliability of information available on a given situation. Based on this, management decisions can be made both under conditions of certainty (deterministic decisions) and under conditions of risk or uncertainty (probabilistic decisions).
Management decision making process is a cyclic sequence of actions of a management subject aimed at resolving the problems of a given organization and consisting in analyzing the situation, generating alternative options and choosing from them the best option, and then - the implementation of the chosen management decision.
The practice of preparing and executing management decisions provides numerous examples of errors at all levels of economic management. This is a consequence of many reasons, since economic development consists of a large number of different situations that require resolution.
The most important place among the reasons for the adoption and implementation of ineffective management decisions is ignorance or non-compliance with the technology for their development and organization of their implementation.
An important role is played by the cybernetic approach to the development of management decisions, which has become known as a theory of decision making. It is based on the widespread use of mathematical apparatus and modern computer technology.
All management decisions can be divided into two types:
- - traditional solutions that have taken place many times before, in this case one should choose one of the already available alternatives;
- - non-traditional, non-standard management decisions, their development is associated with the search for new alternative options.
In this regard, traditional, typical, repetitive management decisions can be formalized, that is, they can be made and implemented according to a predetermined algorithm. Consequently, a formalized management decision is the result of performing a pre-established sequence of actions. For example, when a repair schedule for machinery and equipment is drawn up, they proceed from a standard that determines the relationship between the amount of equipment and the number of repair workers. So, if in machine shop If this organization operates one hundred units of equipment, and the standard for its maintenance is 10 units per repair worker, then this workshop should contain ten repair workers. Further, if the issue of investing in securities is being decided, then a choice is made of their individual types based on which securities provide the opportunity to receive the maximum profit per invested capital.
As a result of the formalization of decision-making, the level of management efficiency increases by reducing the likelihood of making an error, as well as by saving time, since there is no need to develop this solution starting from scratch.
As a result, the management of the organization tries to formalize management decisions in case of those situations that are systematically repeated in the activities of this organization. Formalization of management decisions consists in the development of certain rules, instructions, standards that allow making and implementing competent management decisions.
Along with recurring situations, there are also atypical situations that have not been encountered before and cannot be resolved formally.
Most management decisions are between these two types, which makes it possible to use both formalized methods and the own initiative of the developers of these decisions when making these decisions.
The quality and effectiveness of management decisions are determined by the degree of validity of the methodology for solving problems, namely approaches, principles and methods.
Analysis of organizational management makes it possible to determine the need to use different approaches.
The systems approach to management assumes that any system or object is considered as a set of interconnected components that has an output, that is, a goal, an input, a connection with the external environment, and feedback. In such a system, the “input” is transformed into an “output”.
In terms of use integrated approach enterprise management must take into account technical, environmental, economic, organizational, social, psychological, political, demographic areas of management, as well as their relationships.
If at least one of these areas is not taken into account, then a complete solution to this problem will not be achieved. Unfortunately, in reality, as a rule, an integrated approach is not followed. Thus, in the context of the construction of new enterprises and organizations, the solution social problems is often postponed. This delays the commissioning of this facility or causes its partial use. Other examples can be given. Thus, in the process of designing new equipment, insufficient attention is paid to its environmental friendliness, which leads to the non-competitiveness of this equipment.
The integration management approach involves studying and strengthening the relationships between individual subsystems and elements of the management system, as well as between stages life cycle control object, between individual levels of control vertically, and, finally, between individual control subjects horizontally.
The marketing approach of management provides for the orientation of the management subsystem towards the consumer in the context of solving any problems. Main criteria marketing approach are:
- - improving the quality of the management object in accordance with consumer requirements;
- - saving money for the consumer by improving quality;
- - saving resources in own production due to factors of production scale, scientific and technological progress, as well as the use of a scientifically based management system.
The functional approach to enterprise management is that any need is considered as a set of functions that should be performed to satisfy it. Once functions are defined, several alternative objects are created to implement those functions. Then, one of these objects is selected that requires a minimum of total costs during the life cycle of this object per unit of its beneficial effect.
The essence of the dynamic management approach is that when it is applied, the control object is considered in its dialectical development, in its cause-and-effect relationships. Here, a subsequent retrospective analysis is carried out for 5-10 or more past years, as well as a prospective (forecast) analysis. The reproduction approach to enterprise management is focused on the constant resumption of production of this type of product in order to meet market needs. Wherein this type products must have lower total costs per unit of beneficial effect than the best similar product on the given market. The main elements of the reproductive approach are the following:
- - use of a leading comparison base when planning the renewal of this type of product;
- - saving the amount of past, living and future labor during the life cycle of a given type of product per unit of its beneficial effect;
- - consideration of the relationship between manufactured, designed and future models of this type of product;
- - reproduction of elements of the external environment proportional in quantity (mainly the macro-environment of a given country and the infrastructure of a given region);
- - integration of science and production in large organizations.
The process approach to organization management considers management functions in their interrelation. The management process is total amount all functions, that is, it is a series of continuous interrelated actions. The normative management approach consists of establishing management standards for all its subsystems. These standards should be determined by the most important elements:
- - target subsystem (it covers indicators of quality and resource intensity of products, market parameters, indicators of the organizational and technical level of production, indicators social development team organization, environmental protection indicators);
- - supporting subsystem (standards for providing employees, as well as individual divisions of the organization, with everything necessary for successful work, for fulfilling the tasks facing them, standards for the efficiency of use individual species resources for the organization as a whole);
- - functional subsystem (standards for the quality of plans, organization of the management system, standards for the quality of accounting and control, standards for stimulating high-quality work).
The listed standards must meet the requirements of complexity, efficiency, and prospects.
As for the standards for the functioning of elements of the external environment, the organization does not control these standards; however, it must have a bank of these standards and strictly comply with them, especially legal and environmental standards.
The organization must also take part in the formation and development of a system of environmental standards.
The essence of the quantitative management approach is the transition from qualitative to quantitative assessments using mathematical and statistical methods, engineering calculations, expert assessments, a point system, etc.
The administrative (directive) approach to enterprise management involves the regulation of functions, rights, responsibilities, and quality cost standards.
The main task of the behavioral approach to managing an organization is to increase the efficiency of the organization by improving the use of its labor resources. The use of behavioral science helps improve the performance of both individual employees and the organization as a whole. The fact is that as a result of the application of behavioral science to the management of an organization, individual employees are helped to understand their capabilities and creativity, which ultimately leads to increased efficiency of the organization.
The essence of the situational approach to enterprise management is that the degree of suitability of individual management methods is determined by the specific situation.
Since there are many factors influencing the activities of an organization, both internally and externally, it is impossible to find a single best way management. The most effective method in a given situation will be the one that best suits the current situation.
These are the main approaches that determine the quality and effectiveness of management decisions.
1. Classification of management decisions
Describe the presented classifications of management decisions:
Based on the basis of acceptance: intuitive, based on judgment, rational;
According to the degree of impact on the object: operational, tactical and strategic;
By order of adoption: individual, collective and collegial;
According to the criterion of novelty: routine, selective, adaptive and innovative;
According to the degree of regulation: directive, guiding and recommending;
According to the style of decision-making - according to the ratio of efforts at the stage of developing alternatives and their selection: inert, cautious, balanced, risky, impulsive.
Present and characterize three more approaches to the classification of management decisions (10 classifications in total).
Give examples of each listed classification of management decisions.
The classification of management decisions according to the degree of impact on the object is presented in Fig. 1.1.
Rice. 1.1 - Classification of management decisions according to the basis for adoption
Intuitive solutionsis a choice made only on the basis of the feeling that it is right. In a complex organizational situation, thousands of choices are possible. A manager who relies solely on intuition, from a statistical point of view, has a chance of right choice without any application the logic is low.
Example:
When making a purely intuitive decision, people base it on their own feeling that their choice is correct. There is a “sixth sense” here, a kind of insight, usually visited by representatives of the highest echelon of power. Middle managers rely more on computer information and assistance. Despite the fact that intuition becomes sharper along with the acquisition of experience, the continuation of which is precisely high post, a manager who focuses only on it becomes a hostage to chance, and from a statistical point of view, his chances of making the right choice are not very high.
Decisions Based on Judgmentis a choice based on knowledge or accumulated experience. A person uses knowledge of what has happened in similar situations previously to predict the outcome of alternative choices in an existing situation. However, we note that a leader who is overly committed to judgment and accumulated experience may consciously and unconsciously avoid interaction with new technologies and developments, which leads to irrational decision making.
Example:
A decision to give the competent secretary the authority to respond to all routine correspondence without external oversight. The manager's decision on where to build a warehouse for finished products.
Rational decisionis a decision that is based on the basis of the analytical process, and is often independent of previous experience.
Stages of making a rational decision: diagnosis of the problem, formulation of restrictions and criteria for decision-making, identification of alternatives, analysis and evaluation of alternatives, final selection of an alternative, implementation of the solution, feedback, evaluation of results.
Example:
Choosing (purchasing) a car. Selecting a product market based on the conducted marketing research.
The classification of management decisions according to the degree of impact on the object is presented in Fig. 1.2.
Rice. 1.2 - Classification of management decisions according to the degree of impact on the object
Strategic management decisions- these are decisions that are made at the highest level of management for the long-term development of the organization. Such decisions are followed by the development of: a strategic plan, the production program of the organization. Strategic decisions involve fundamental changes in the organization: changing the directions of financial flows into product groups or target segments, transforming the structure, entering new regional markets, expanding or reducing activities, changing assortment policy. Strategic management decisions are made at the level of directors, vice-presidents of the company, deputy. directors, heads of production departments and workshops. In a small business, all responsibility for making strategic decisions is concentrated in the hands of the manager and his team.
Strategic are directive acts that direct, organize and motivate the collective actions of people to achieve strategic goals. Strategic planning includes:
developing policies in various areas that determine the life of the organization;
development of programs and projects, forecasting and determination of socio-economic development.
Strategic management decisions are designed to ensure that the organization fulfills its mission and, due to this, its survival in a highly competitive environment.
Example:
A car manufacturing plant is deciding whether to produce any spare parts for the cars itself or find a supplier from which to purchase them.
Operational management decisionsperform a corrective role directly in the course of the production activities of the enterprise, solving suddenly arising problems that cannot be delayed.
Operational management decisions are made daily based on the conditions of production activities, resource availability, market demand, prices, social demands, events in the political, economic, social, environmental environment. Feature: operational decisions are sensitive to emerging unforeseen situations, and therefore they are called situational.
Subject of operational decisions: organizational measures, urgent orders, replenishment of emerging losses, damages, replenishment of missing material, labor, financial resources, adjustment of planned, program activities, obtaining current benefits.
Programmed decisions have the greatest weight in the totality of operational management decisions, since operational decisions are fleeting, urgent, and require the fastest possible execution and immediate response to the situation.
Example:
Repairing a broken machine in the workshop. Repairing a computer in the office. Software installation.
Tactical management decisions, as a rule, are focused on the short and medium term and problems of a production and technical nature.
Tactical management decisions are associated with medium-term problems, the development of a line of action for a relatively short period of time in accordance with the developing situation in production and markets. Tactical decisions are a way of concretizing a strategy, translating it into specific measures to be implemented during a certain planning, program period.
Orientation of tactical management decisions: as a rule, such decisions are aimed at achieving intermediate goals, solving problems that contribute to promotion and general goals.
Example:
Decisions of the company (manager) on the terms on which the enterprise will agree on supplies necessary equipment(software).
Operational and tactical decisions are related to the implementation of current goals and objectives. In terms of time, they are designed for a period not exceeding a month.
The classification of management decisions according to the order of adoption is presented in Fig. 1.3.
Rice. 1.3 - Classification of management decisions by order of adoption
Collegial decisionis a decision made by a group of managers and specialists.
As a rule, decisions are made by the head of the organization in agreement with leading top managers and specialists, collectively. This happens in most companies. The manager delegates parallel powers or uses the technique of mandatory approval, which is stated in administrative documents as “agreed”. With mandatory approvals, responsibility for making significant decisions partially rests with the managers who assume such authority. Parallel powers increase the responsibility and rights of managers, and the decision becomes collective. For example, many companies use concurrent authorities to control financial expenditures, and large purchases require two or three executive signatures.
Collective decisions are usually made at business meetings and during the work of commissions by leading managers and specialists. At such meetings there is already a known balance of power, which significantly influences the management result, the decision.
Example:
The manager attracted external law firm for advice on any legal issues.
Collective (democratic) decisions- these are decisions made by the majority of the organization’s employees, jointly by the work collective or by a small group. Unlike collegial ones, democratic decisions are a clear expression of the will of the majority of members of the work collective, small or large. Such decisions are made through secret voting, using expert assessment methods, for example, nominal group technique, Japanese ring techniques. The use of such methods is possible with a high level of staff motivation, the use of a democratic leadership style, and a developed and transparent corporate culture.
Collective decisions are also made when significant problems and issues that affect the entire staff are raised.
Example:
Election of a manager by competition, introduction of a new remuneration system, etc.
Individual management solutionsThese are decisions that are made by the manager alone. Small business organizations have a small number of management levels and a high risk of losing competitive status. Such an organization is led by an entrepreneur who bears full responsibility for its further functioning in unstable market conditions. An entrepreneur is afraid to delegate authority on financial and other significant issues to his subordinates and makes decisions alone. The positive aspect of an individual solution is its creative, extraordinary nature.
The disadvantages of individual decisions appear when they acquire an authoritarian character. The leader usurps power, individually manages resources, determines personnel policy organization and puts pressure on subordinates. Decisions made by the manager alone allow the organization to remain in the market for some time and be successful. However, in the future, the leadership style used by the leader hinders the development of the organization. A leader must be able to maneuver and be flexible, use the art of delegating decision-making powers to other people in the organization.
Example:
The manager decided to prepare presentation material for the meeting on his own, without resorting to the help or cooperation of employees.
The classification of management decisions according to the criterion of novelty is presented in Fig. 1.4.
Rice. 1.4 - Classification of management decisions according to the criterion of novelty
Routine solutionsare adopted in accordance with the existing program, the manager must identify the situation and take responsibility for starting certain actions. Difficulties can arise here if the manager is incompetent, misinterprets existing indications of a particular situation, acts illogically, or shows indecisiveness. A leader who correctly perceives the situation, draws the right conclusions, acts intelligently and controls the consequences, achieves what is expected of him. At this level, no creativity is required since all procedures are pre-prescribed.
Example:
Where to place the computer on the desktop.
At selective solutionsa certain amount of initiative and freedom of action is required, but within certain limits. Selective decisions imply that the manager evaluates the merits of a whole range of possible solutions and tries to choose those actions that best suit the given problem and are the most effective and economical.
Effectiveness depends on the manager's ability to select the course of action with the highest probability and whether it turns out to be acceptable, economical and effective.
Example:
Selection (rather than development of a new) system of motivation and incentives for personnel.
Adaptive solutionscause difficulties, since here the manager is looking for a new solution to a known problem, must be able to abandon the usual, but already outdated approach to the problem and develop a creative solution. The success of a leader depends on his personal initiative and ability to make a breakthrough into the unknown. Such solutions provide an answer that could have existed before, but in a different form. A manager is looking for a new solution to a known problem.
Example:
Innovative solutionsare the most complex, the leader needs to find ways to understand completely unexpected problems, and solving such problems requires new ideas and methods, the ability to think in new ways, the ability to creatively solve the problem by discussing and using creative ideas other specialists.
A manager must be able to understand completely unexpected problems, the solution of which requires the manager to develop thinking in relation to changing conditions. It is possible that solving today's complex problems may require the creation of a new branch of science or technology.
Development of a new (innovative) approach to organizing and conducting conference calls, for example, via IP telephony or Skype.
Classification of management decisions by content in Fig. 1.5.
Rice. 1.5 - Classification of management decisions by content
Solutions with quantitative characteristics, are accepted on the basis of mathematical and statistical methods. The assessment of quality and efficiency in this case is simplified, since the achieved level is compared with the planned one.
Example:
Reduction of finished product defects by 5%.
Solutions that are not quantitative, are subjective in nature, as they are determined by the personality of the subject receiving them. Assessing their quality is complex and quite controversial, since it is also subjective.
Example:
Carrying out the procedure for rotation (rearrangement) of personnel of the enterprise
The classification of management decisions by degree of regulation is presented in Fig. 1.6.
Rice. 1.6 - Classification of management decisions by degree of regulation
Policy decisionsmust be carried out and do not imply any initiative. They establish a clear relationship between certain parameters and specific solution options.
Example:
Making a decision on the introduction of information and communication technologies in the field municipal government will be directive for those responsible for its implementation.
Orienting solutionsdetermine possible options activities of employees upon the occurrence of certain conditions.
Example:
The decision will be a guide for archive workers, as it tells them that soon the work of many of them will not be in demand. At the same time, it provides for the training of specialists to work with the municipal information system.
Example:
The same decision for different categories of performers can be directive, guiding and recommending.
The classification of management decisions by decision-making style is presented in Fig. 1.7.
Rice. 1.7 - Classification of management decisions by decision-making style
The nature of the development and implementation of management decisions strongly depends on the personal characteristics of a person.
Balanced Solutionsaccepted by managers who are attentive and critical to their actions, put forward hypotheses and their testing. They usually have an initial idea formulated before making a decision.
Example:
Despite the complaints of some members of the team against their immediate supervisor, the director does not apply sanctions against him, since the complaints turned out to be rumors spread on purpose.
Impulsive decisionsare accepted by managers who easily generate a wide variety of ideas in unlimited quantities, but are unable to properly test, clarify and evaluate them. Therefore, decisions turn out to be insufficiently substantiated and reliable; they are made “at once”, “in jerks”.
Example:
Dismissal of a manager against whom there are unverified complaints from his subordinates.
Inert solutions- the result of a careful search. In them, control and clarifying actions predominate over the generation of ideas, so it is difficult to detect originality, brilliance, and innovation in such decisions. They weakly motivate staff to implement them.
Example:
Conducting an internal audit
Risky decisionsare accepted without careful justification of actions by a leader who is confident in his abilities. Typically, such managers have good support in the form of constantly supporting superior managers or subordinates. They may not be afraid of any dangers.
Example:
Careful decisionsare characterized by the manager’s thorough assessment of all options, a hypercritical approach to business, big amount approvals. Such management decisions are effective in resolving problems relating to human life and their environment.
Example:
The decision to increase travel expenses for the company's lawyer after conducting all possible comprehensive analysis of his presence and absence at preliminary hearings on various lawsuits and the consequences of these trips.
Classification of management decisions by content management process shown in Fig. 1.8.
Rice. 1.8 - Classification of management decisions according to the content of the management process
Economic solutionsassociated with the management system, necessary for increasing the economic efficiency of the organization’s activities, profitability, payback and liquidity of assets. How best to manage resources, make the enterprise profitable, increase profits - these and other questions will confront the manager making economic decisions.
Economic management decisions are manifested in the fact that the development and implementation of any management decision requires financial, material and other costs. Therefore, every management decision has a real cost.
The implementation of an effective management decision should bring direct or indirect income to the company, and an erroneous decision or a decision misunderstood by subordinates leads to losses and sometimes to the cessation of the company's activities.
Example:
If a manager decides to fire a negligent employee, the latter may suffer greatly, and if he does not fire or take other measures, the entire organization may suffer.
Social solutions- These are decisions that affect the organization's social structure, personnel, corporate culture, climate and shared values. Social decisions can be related to optimizing the work of personnel, improving the system of motivation and social support for employees, the image of the organization in society, and the implementation of the mission.
Example:
Promotion wages, introduction of environmentally friendly equipment, improvement of sanitary conditions, strengthening of safety requirements, conflict resolution.
Organizational decisions- these are decisions related to management methods, ways to achieve goals. Such decisions are an integral part of the management process.
The essence is that company personnel are involved in this work. To work effectively, it is necessary to form an efficient team, develop instructions and regulations, vest workers with powers, rights, duties and responsibilities, establish a control system, allocate the necessary resources, including information, provide workers with the necessary equipment and technology, and constantly coordinate their work.
Example:
Organize workers to complete the task, redistribute functions and powers, carry out general meeting.
Technical solutions- these are operational decisions that are necessary to ensure labor and production processes, supply the necessary resources, materials, and information.
Example:
Install software in the department, replace a broken machine, pay travel expenses, send an employee to an important production area.
The classification of management decisions according to the method of fixing the management process is presented in Fig. 1.9.
Rice. 1.9 - Classification of management decisions according to the method of fixing the management process
Management decisions can be expressed in in writingHow administrative documents in the form of orders and instructions. Managers provide written decisions for legal review and subsequently for execution.
Example:
Order for hiring a new employee
In extreme circumstances, the oral form is used. The disadvantage of this method is that performers sometimes distort the content, and not always consciously, and interpret the decision in their own way.
Verbal management decisionsalso have legal force, and they can be appealed in court if there are at least two people who heard these decisions.
Oral management decisions occur during meetings, conferences and business conversations. Meetings and deliberations are collective events (public or involving a wide range of participants); conversations are mostly conducted individually or with a small number of people gathered.
Example:
Verbal order to establish a work schedule on a day off
Electronic solutions involves recording decisions on electronic media. This method allows you to use all the capabilities of information and communication technologies. After acceptance Federal Law No. 149-FZ of July 27, 2006 “On information, information technologies and information protection”, the electronic method of recording decisions has become widespread.
Example:
Providing by a manager to a subordinate through Email documentation for negotiations
In the practice of enterprises from the position legal registration management decisions The most common are written management decisions.
The classification of management decisions by information processing method is presented in Fig. 1.10.
Rice. 1.9 - Classification of management decisions by information processing method
Algorithmic solutionsinvolve strict formalization of the implementation of procedures and operations based on rules, algorithms, formulas, and statistical data.
Example:
Calculation of the economic efficiency of new production should be carried out using developed algorithms.
But in management, not everything can be measured quantitatively. Something is assessed qualitatively. You can process and evaluate information based on intuition, generalizations, ideas, experience, and associations. Through conversation, discussion, and asking leading questions, you can obtain new information from a client or partner. Such solutions are called heuristic.
Example:
Receiving information from a partner about discounts received on office paper from the same supplier stationery.
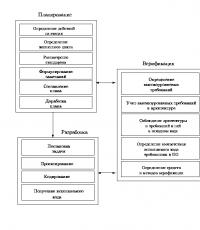
2. Target and processor technologies
management business processor
Target technologies
Provide examples of the use of each of the target technologies both in business and in the field of educational and extracurricular activities at the university. Provide at least two examples for each area.
Processor technologies
Provide at least two examples of the use of each processor technology.
Target technologies
Target technologies are technologies based on the priority of goals over situations. Target technologies focus decisions on achieving a goal, rather than eliminating disturbing influences.
The classification of target technologies is presented in Fig. 2.1.
Regulatory technologyconsists of issuing tasks (goals, tasks) for execution, indicating the means and their possible limitations, recommended methods and the estimated time for their implementation. The technology provides for strict control of the process of approaching the target.
The professionalism of completing a task is determined by the qualifications of the manager who issued the task and the performer. This implies strict control over the positive dynamics of the task completion process.
Regulatory technology can lead to two main results:
achieving tangible positive results from the process of achieving the goal;
lack of significant positive results within an acceptable time (treading water).
Regulatory technology involves development by the head ultimate goal management and strategies with possible limitations of various resources (material, human, financial, etc.). In this case, the goal will definitely be achieved, but within a time frame that is difficult to determine in advance. Achieving the goal is guaranteed only with strict internal or external control of the progress of the process of realizing the set goals.
the time for completing the goal or its component tasks should not be precisely specified (the process of achieving the goal itself is important);
there may be a significant and unpredictable limitation of resources (financial, technological, raw materials, etc.);
innovative and long-term nature of developments;
The estimated time to achieve the goal is over 1 year.
This technology is based on statistical methods, fuzzy set theory, and the theory of developing solutions under conditions of uncertainty. The authorship of the program and the results obtained belongs to the director and performer.
Example:
Writing a book. Preparation and writing of student work (graduation project, course work and etc.).
Drawing up a business plan.
Initiative-target technologyis based on issuing tasks without specifying the means and methods for their implementation and is designed for an initiative and professional performer.
Initiative-target technology involves the development by the manager only of the final goal of the task for an employee or department, as well as the deadline for completion, without indicating the mechanism for achieving it. In this case, the goal may not be achieved for some reason, it may be achieved within the stipulated time frame or earlier, or it may be achieved outside the established period.
Initiative-target technology gives great scope for initiative decisions of subordinates.
Basic conditions for using this technology:
the staff of the organization or its division is no more than 10 people;
the time required to complete the assignment should not exceed one month from the date of its issuance;
high professionalism of the staff or great confidence in them on the part of the manager;
production of new goods, services, information or knowledge;
the presence of stable informal relationships in the team.
The professionalism of the task is determined by the qualifications of the task performer, and the qualifications of the manager play a secondary role. Technology does not guarantee achievement of the goal.
Example:
In the process of completing the task assigned by the manager to the employee, the specialist quit, which resulted in a significant reduction in the necessary resources.
For decreasing occupational diseases The company's management decided to purchase technology that does not use asbestos as fillers for building blocks, and they decided to “freeze” the construction of a new technological building.
Software-targeted technologyused most often in organizations. It consists of issuing tasks (goals, tasks) for execution, indicating the means, methods and time for their implementation, there are instructions on external or internal control intermediate states of this execution.
The professionalism of completing a task is determined by the qualifications of the manager who issued the task, and the qualifications of the performer play a secondary role. Software-targeted technology usually guarantees the achievement of the goal.
The use of software-targeted technology can lead to three main results:
achieving the goal within a given time frame with acceptable deviations from the given intermediate values;
achieving the goal within a given time frame with significant deviations from the specified intermediate values;
consistent failure to achieve a goal within a given time frame.
This technology involves the development by the manager of management goals, means and methods for their implementation, as well as the timing and states of intermediate process values. If any given intermediate value is not achieved, then additional resources are allocated for its implementation; if the given intermediate value exceeds the planned one, then part of the resources is transferred to other needs and the goal will be achieved within the stipulated time frame.
Program-target technology is based on modern knowledge, economic and mathematical methods and information technologies.
Basic conditions for using this technology:
certainty and availability of management and production resources;
clearly expressed separation of management and production;
a large volume of standard procedures, situations and solutions.
Example:
When developing a political platform for a political organization in which its leader is the ideologist and conductor of a set of activities. In this case, the qualifications of the performer play a secondary role, and the professionalism of the task is determined by the qualifications of the manager who issued the task.
Development and implementation, for example, of the Federal Target Program " State border Russian Federation»
Processor technologies
For successful implementation, each target technology for developing management decisions has its own set of processor technologies that represent the mechanism for implementing the target technologies.
The processors include six control technologies (see Fig. 2.2).
Rice. 2.1 - Classification of target technologies
Results-based management technologybased on the priority of final results over planning and forecasting. The main function performed by managers is coordination (adjustment) of actions and decisions depending on the results obtained.
This technology is well implemented for medium and small organizations or divisions in which:
the time between decision-making and the result of their implementation is minimal (hours, several days);
there are no insurmountable difficulties in quickly acquiring the required resources or returning unclaimed ones;
the professionalism of the head of the organization or the project manager is quite high;
The nature of production is predominantly mechanized.
The basis of this technology is a business plan and developments for making management decisions under conditions of possible uncertainties. It is known that the most necessary factors for developing an effective management decision are either unknown or precisely indeterminable.
This technology is the cheapest among other technologies, since it does not require the development of detailed plans and the calculation of funds for the implementation of solutions.
Example:
1. solution and writing independent work on the exam.
Planning a report on the annual sales volume of products (services).
Management technology based on needs and interestsis based on the priority of interpersonal relationships over other means and methods for forming interaction between employees participating in the implementation of the goal.
Interaction between a manager and a subordinate when implementing this technology can only occur if the impact affects the needs and interests of both the manager and the subordinate. All other options lead to resistance from the subordinate.
This technology is effectively implemented in large and medium-sized organizations in small regions (cities, towns, etc.), where the organization’s activities significantly affect the municipal infrastructure.
The number of personnel involved in this technology is not limited. The main function performed by managers is planning and organizing interaction between participants in the labor process; a positive result is guaranteed.
Example:
Creation of an enterprise in cities and towns with developed textile industry, where one large organization gives birth to a number of smaller service enterprises.
Opening of a new city library in a place where there is no public transport
Control technology through constant checks and instructionsis based on the priority of control and strict personnel management over other means and methods for forming interaction between employees participating in the implementation of the goal. Control and strict management are justified by the fact that in this case a person better realizes his needs for self-expression, self-display, stability and order.
This technology is effectively implemented in small organizations in which the authority and professionalism of the manager is beyond doubt, especially in new knowledge-intensive organizations, educational institutions or in enterprises where consultant-managers work on a contractual basis.
Example:
1. Conducting testing, certification, exams, testing the knowledge of students by the teacher.
Choreography for the play. In this case, the group leader (choreographer) is the authority who regulates and controls every movement of the dancer (actor).
Control technology in exceptional casesis based on the priority of the professionalism of performers or proven and well-executed production technology over other means and methods for the successful completion of assigned or selected tasks.
This technology is effectively implemented in small organizations that work either using strictly regulated technology or in organizations with a trust (functional) management structure.
In this structure, the manager exercises linear influence in all areas production process in administrative functions, and in economic, technological and other functions, provides the required assistance to subordinates and colleagues. The leader is in a situation: an equal among equals. The contractor can also transfer part of his work to a lower level and act in relation to him as a line manager and as an adviser.
Example:
1. The accountant fulfills the instructions of the chief accountant to prepare and submit reports to the director of the enterprise.
Instruction from the teacher to the student to carry out public lesson.
Control technology based on “artificial intelligence”is based on the priority of proven practice, statistics and modern economic and mathematical methods, implemented in the form of knowledge bases or databases using modern information computer technologies.
This technology is especially effective for any organizations with a large volume of standard complex procedures.
Example:
Filtering email using a computer. In this case, the most important letters are first submitted for consideration to the head of the enterprise.
Maintaining logs of student progress in universities.
Management technology based on the activation of personnel activitiesis based on the priority of incentives and rewards for the employee over other means and methods for the successful completion of assigned or selected tasks. It is mainly effective when manual production, when labor productivity and quality of products are mainly determined by the mood, psychology and health of the employee, as well as the socio-psychological climate in the team. The number of employees is unlimited. Technology requires a system for monitoring the effect of incentives and rewards on the activities of each employee or team.
This technology influences the satisfaction of the needs and interests of employees not directly from the manager, as in management technology based on needs and interests, but through the decisions of the employee himself. Technology requires a high level vocational training HR specialists.
Example:
Incentivizing an employee by giving him a responsible task or paying remuneration in cash and (or) commodity forms.
Writing essays, independent study of educational literature as a student’s motivation to receive automatic final grades for the semester (year).
List of used literature
1.Abryutina M.S., Grachev A.V. Analysis of the financial and economic activities of the enterprise. - M.: Publishing House “Business and Service”, 2010. - 256 p.
2.Baldin K.V., Vorobiev S.N., Utkin V.B. Management decisions: Textbook. - M.: Dashkov and K, 2007. - 496 p.
.Batrick R. Techniques for making effective management decisions: Textbook. - 2nd ed. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2010. - 416 p.
.Vertakova Yu.V., Kozyeva I.A., Kuzbozhev E.N. Management decisions: Tutorial. - M.: KnoRus, 2009. - 352 p.
.Vertakova Yu.V. Management decisions: development and choice: Textbook. - M.: KNORUS, 2010. - 422 p.
.Garkusha N.M. Models and methods of decision making in analysis and audit: Textbook / Ed. N.M. Garkushi, O.V. Tsukanova, O.O. Goroshanskaya. - 2nd ed. - K.: Knowledge, 2012. - 591 p.
.Golubkov E.P. Technology of management decision making: Textbook. - M.: Delo, 2010. - 544 p.
.Zlobina N.V. Management decisions: Textbook. - Tambov: TSTU, 2007. - 80 p.
.Kokoreva T.A. System analysis of decision-making procedures. - M.: Timber Industry, 2009. - 290 p.
.Litvak B.G. Development of management decisions: Textbook. - 3rd ed. - M.: Delo, 2011. - 288 p.
.Litvak B.G. Development of a management solution. - 4th ed., rev. - M.: Delo, 2012. - 392 p.
.Mashchenko V.E. Systemic corporate governance: Tutorial. - M.: Sirin, 2013. - 251 p.
.Raizberg B.A., Lozovsky L.Sh., Starodubtseva E.B. Modern economic dictionary. - 5th ed., revised. and additional - M.: INFRA-M, 2007. - 495 p.
.Smirnov E.A. Development of management decisions: Textbook. - 2nd ed., add. - M.: 2012. - 271 p.
.Smorchkov A.V. Development of management decisions: Textbook. - Part 2. - Bryansk: BSTU, 2011. - 44 p.
.Travin V. Preparation and implementation of management decisions: Textbook. - M.: Delo, 2008. - 80 p.
.Fatkhutdinov R.A. Management decisions: Textbook. - 5th ed. - M.: INFRA-M, 2008. - 314 p.
.Shemetov P.V., Radionov V.V., Cherednikova L.E., Petukhova S.V. Management decisions: Textbook. - 2nd ed., add. and revision - M.: Omega-L, 2012. - 400 p.
Tutoring
Need help studying a topic?
Our specialists will advise or provide tutoring services on topics that interest you.
Submit your application indicating the topic right now to find out about the possibility of obtaining a consultation.
A management decision is the result of a specific management activities manager A managerial decision is a choice that a manager must make in order to fulfill the responsibilities of his position. The purpose of such a decision is to ensure movement towards the tasks assigned to it. Therefore, the most effective management decision is the choice that will actually be implemented and will make the greatest contribution to achieving the final goal.
Subject of SD adoption– a person or group of people (managers) making decisions. Object of execution of management decision– a person or group of people in an organization who implements a decision. Purpose of management decision– ensuring movement towards the goals set for the organization. The more effective a solution is, the greater its contribution to moving toward the organization's goals. Management methods: decision tree - schematic representation of a decision-making problem. Brain attack undertaken by a group as an idea generation process where all possible alternatives are considered from a critical perspective. Nominal group method limits discussions or communication with each other to a certain extent. Group members attend the meeting but act independently.
Classification of decisions based on the methods used to make them. Customized solutions. Consulting solutions. Group solutions. The leader consults with other people and chooses the best solution.
Classification of management decisions by the nature of goals. Exist strategic decisions ( main tasks). Tactical decisions ( private problems). ABOUT operational solutions ( urgent tasks).
● By scale level. Decisions can be made at various levels: national economic, covering several or all sectors of the national economy; corporate, covering several enterprises; enterprise level; department level; department level; brigade level, etc.
● By content. The decisions made may relate to certain activities of the enterprise: economic, technical, social, organizational, etc. Economic decisions are related to increasing production efficiency and improving the activities of the enterprise. Technical decisions are made to improve production technology. Social solutions are aimed at improving working conditions. Organizational decisions are aimed at improving the organization of work.
● By duration of action. Decisions can be made for a long period (5 years or more), being strategic in nature. Solutions can also be medium-term - designed for a year or quarter; short-term, designed for a month, a week and a day. Short-term decisions include current, operational decisions made to resolve current, private situations. The number of operational decisions made in an organization, as a rule, significantly exceeds the number of strategic decisions.
● According to the form. Decisions can be documented - in the form of a letter, diagram or drawing and undocumented (oral). Most decisions in the management apparatus are documented, but small, insignificant decisions, as well as decisions made in emergency situations, may not be recorded in the form of documents.
● By degree of uniqueness. Solutions are distinguished between routine, optimal, rational, and innovative.
35.Methods of personnel management. Personnel management is an activity aimed at providing an organization with high-quality personnel capable of performing the labor functions assigned to them and their optimal use. The process of effective use and development of an enterprise’s human resources to achieve organizational and personal goals of personnel, through the use of economic, organizational and socio-psychological methods management.
Human resource management is divided into the following areas of activity: search operational work with personnel (including training and development of personnel, operational assessment of personnel, labor organization, management business communications, motivation and remuneration), strategic work with personnel.
Methods: economic methods - techniques and methods of influencing performers using a specific comparison of costs and results (material incentives and sanctions, salary) The following methods are economic:
technical and economic analysis; economic incentives; work motivation; remuneration; participation in profits and capital; participation in property;; organizational and administrative methods - methods of direct influence, which are mandatory, they are based on various instructions and guidelines, acts in force in the organization; socio-psychological methods (motivation, moral encouragement, social planning). Social-psychological methods include: socio-psychological analysis; creation of a creative atmosphere; participation of workers in management; social and moral stimulation; satisfaction of cultural and spiritual needs; creation of a normal psychological climate;
HR specialist - HR manager (HR specialist). Enterprises sometimes delegate some HR management functions to specialized recruitment agencies. Personnel Management- part of management associated with the labor resources of the enterprise and their relationships within the company. It is a special form functional activity aimed at the most effective use of employees’ potential to achieve the goals of the enterprise and their personal goals. The main goals of personnel management are: meeting the enterprise's personnel needs; ensuring rational arrangement, professional qualification And promotion personnel; effective use of the enterprise's labor potential. The basic principles of using the company's personnel are: compliance of the number of employees with the volume of work performed; compliance of the employee’s qualifications with the degree of complexity of his labor functions; the structure of the enterprise's personnel is determined by objective factors of production; maximum efficiency in using working time; creating conditions for continuous training and expanding the production profile of workers. The development and movement of personnel is associated with the development and implementation personnel policy, including: planning, attraction, hiring and placement work force; professional education, training and retraining of workers; career planning, promotion and release of personnel; working conditions and remuneration, creation of a favorable psychological climate in the team. Work with personnel at the enterprise is carried out by all line managers, as well as some functional departments, services and individual specialists and managers: personnel department; labor and wages department; technical training department; HR department; NOT laboratories; managers (directors, managers) of personnel (personnel).
Question 36: Firm resources and their classification. The enterprise in the process of production activities uses a large number of resources: land, labor, financial, material, production, technological, mental.
All resources used in the production process can be classified:
By origin;
By nature of use;
By playback method;
With participation in production.
Resources are also divided into:
Natural (this includes land, water, forest, solar and wind energy and others);
Economic (this includes means and funds that are used in the production process: tractors, cars, production machines, combines and other mechanisms used in the production process).
According to the method of reproduction, enterprise resources are divided into:
Regenerative (resources that, when used, are capable of self-regeneration, these include solar and wind energy, water resources);
Non-renewable (these are resources that are not restored during use; these include material resources, land resources, production and other resources).
With participation in production, the enterprise's resources are divided into:
Functional (these are those resources that are directly involved in the production process);
Reserved (these are resources that cannot be used for one reason or another).
Resources – this is everything that can be used by a company to achieve its goals, to meet its own needs and the needs of subjects of the external environment.
With some simplification, which does not particularly affect the understanding, we can say that resources– this is everything that is presented in the asset balance of the company. Those. resources include fixed assets and intangible assets, work in progress, inventories of materials and goods, cash, accounts receivable, etc.
TO financial resources includes cash, accounts receivable, securities, financial investments, participation in the authorized capital of other organizations, etc. Their peculiarity is that they cannot be used (consumed) directly within the company. Likewise, they cannot be created within the company. These resources are used and created when the company interacts with the external environment. (To spend money or buy securities, you must carry out a business transaction with the participation of some other company or organization.) Thus, financial resources reflect the company’s relationship with the external environment.K production resources include materials, labor resources, in-production work and services, finished products, etc. The peculiarity of these resources is that they can be used (consumed) directly within the company and/or created within the company. in production processes or are the result of these processes.
Which resources - financial or production - are most important to us? If we are talking about the success of the company in general, then we equally interesting both financial and production resources. If we are talking about the success of work from the point of view of profitability, “cost”, then we, of course, are primarily interested in production resources. (Remember? Costs are the cost of the production resources used.) Therefore, let’s “take a closer look” at the production resources.
Resources used- materials, fixed assets, labor resources, in-process work and services - are consumed within the company, i.e. do not go beyond its limits. Output resources- work in progress, finished products, external works and services – are sold (sold) to external clients i.e. go outside the company. (It must be said that the same resource can refer to both used and external resources. For example, thermal energy produced at an enterprise can be used both within the company and provided to external consumers.) In turn, the resources used can be divided for primary and secondary resources.
Primary resources– materials, labor, fuel, services and work from outside, etc. – come to the company from outside. Secondary resources– in-process services created on our own fixed assets, etc. – are created within the company based on the use of primary resources. The company’s activities are a constant “circulation” of resources - financial resources are transformed into production resources, production resources into financial ones, etc.
Question 37: technical and technological resources of the company. Technology is a combination of three elements: tools of labor (machines and equipment), objects of labor (raw materials and materials) and technology (ways and methods of influencing tools of labor on objects of labor to change their consumer properties).
Technology is a method of converting input elements (materials, raw materials, information, etc.) into input elements (products, services). Technology is a way of direct influence of science on the sphere of production. Important characteristic modern technologies is their capacity for inconstancy. Yes, in the area information technologies changes occur even over several months.
The famous American specialist in the field of strategic management Igor Ansoff highlighted three types of technologies according to the level of their inconstancy:
1) stable technology, which practically remains unchanged throughout the entire life cycle of demand (production of canned food and other traditional food products);
2) fruitful technology, which makes it possible to modify products that are produced with its help, constantly improving their ability to meet the needs of consumers (flexible automated systems, rotary lines that are used in mechanical engineering and which are capable of significant readjustment of the working part without changing the basis; computer technologies , in particular software Microsoft Office, each subsequent version of which opens up more and more opportunities);
3) non-permanent (changeable) technology, in which, throughout the life cycle of demand for a product, new basic technologies are used to manufacture it (for example, televisions, while remaining an indispensable attribute of housing, have survived several generations of basic technologies - from lamp to digital).
It is advisable to use a certain technology as long as it is suitable for producing competitive products. In many cases, a basic product sample can be modified and improved, which helps to extend its life cycle, and, consequently, the period of use of the corresponding technology.
The development of new technology is largely determined by the capabilities of the enterprise's existing technical base. Therefore, proceed to technological changes perhaps only by considering the capabilities of existing technology.
The process of systematic and targeted improvement of production technologies and technological equipment characterizes the technical development of an enterprise and predetermines the state of its technical and technological base, on which the results of economic activity directly depend.
38.Financial resources enterprises. Financial resources of enterprises are the totality of their own cash income and receipts from outside, intended to fulfill the financial obligations of the enterprise, finance current costs and costs associated with the development of production. Capital is part of the financial resources invested in production and generating income upon completion of turnover. Sources of financial resources:
a) own (internal):
−income;
− profit from core activities;
−profit from other activities;
−proceeds from the sale of disposed property, minus the costs of its sale;
− depreciation charges;
b) attracted on different terms (external):
− own attracted;
− borrowed funds;
− those arriving in the order of redistribution;
−budget allocations.
It should be remembered that not all profits remain at the disposal of the enterprise; part of it in the form of taxes and other tax payments goes to the budget. The profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise is distributed for the purposes of accumulation and consumption. Profit allocated for accumulation is used for the development of production and contributes to the growth of the enterprise's property. Profits allocated for consumption are used to solve social problems.
Own attracted resources are the result of investments by external investors as entrepreneurial capital.
Entrepreneurial capital- capital invested in authorized capital another enterprise for the purpose of making a profit or participating in the management of the enterprise.
Loan capital (borrowed funds) is transferred to the enterprise for temporary use on the terms of payment and repayment in the form of bank loans,
Issued for different periods, funds from other enterprises in the form of bills, bond loans. Funds raised in the financial market include: funds from the sale of own shares, bonds, and other types of securities. Funds received through redistribution consist of:
− insurance compensation for risks that have occurred;
−financial resources coming from concerns, associations, parent companies;
−dividends and interest on securities of other issuers;
−budget subsidies.
Budget allocations can be used both on a non-refundable and repayable basis. As a rule, they are allocated to finance government orders, individual investment programs, or as a short-term state support enterprises whose production is of national importance.
Financial resources are used by the enterprise in the process of production and investment activities. They are in constant motion and arrive in monetary form only in the form of balances Money on a current account in a commercial bank and the cash desk of an enterprise. In addition to funds formed from profits, integral part the enterprise's equity capital is Extra capital, which, by its financial origin, has different sources of formation: share premium, i.e. funds received joint stock company- by the issuer when selling shares in excess of their nominal value; amounts of revaluation of non-current assets arising as a result of an increase in the value of property during its revaluation according to market value; exchange rate difference associated with the formation of the authorized capital, i.e. the difference between the ruble valuation of the debt of the founder (participant) for the contribution to the authorized capital
39. structure information resources. According to the law of the Russian Federation: information resources are information recorded on a tangible medium and stored in information systems: libraries, archives, funds, other information systems. All information resources (IR) used at the enterprise are intended to support foreign and domestic economic activities. According to the source of acquisition, they are either external to it or internal (corporate). Foreign economic activity is ensured by global (world) IR, and domestic economic activity is ensured by state (national) and regional ones.
Global (world) information resources
Before you decide on foreign economic activity, that is, when an enterprise enters the international market, the entrepreneur must collect information of the following nature: what is the structure and volume of the potential market; what are the specifics of the country, area, climate, traditions, the attitude of buyers towards this or that product; who are the competitors, their characteristics; what are the specifics of business methods in the country; what are the logistics, tariff, customs, tax conditions in the country under study; what are the laws on foreign economic activity in a given country, etc.
Global (world) information resources are available to everyone. They are divided into three groups: business information;
scientific, technical and special; consumer (mass) information.
In turn, business information is divided into: stock exchange and financial: securities quotes, exchange rates, discount rates, commodity and capital markets; statistical information provided government organizations and private companies (economic and social statistics in the form of time series); commercial information on the areas of work of enterprises and firms about their financial condition, product prices, completed transactions, etc.
Information resources in the field of finance and foreign economic activity.
The largest resources: databases on the federal budget and budgets of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, register of passports of import transactions, register of insurance companies (Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation); property register of the Russian Federation (Ministry of State Property of the Russian Federation); database of cargo customs declarations (SCC of Russia); Database " Tax reporting", state register of taxpayers (MTS); fund of licenses for banking and auditing activities (Bank of Russia), etc.
Regional information resources: information resources of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation; urban information resources; municipal information resources.
An enterprise’s information resource is understood to be a collection of its own, acquired and externally supplied data, recorded both on paper and electronic media.
Corporate information resources can be divided into: own; purchased (paid); received from the organization.
The forms of existence of corporate resources can be paper documents, electronic documents, databases, knowledge bases, websites, files of various nature (audio, video), etc.
In essence, information resources are the total amount of data and knowledge circulating in the enterprise, entering it and emanating from it, materialized on any medium.
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted on http://www.allbest.ru/
ANSWERS TO TEST QUESTIONS
1 Option
Question 1. What do you understand by management decision?
Answer. A management decision is understood as the choice of an alternative from a variety of action options. The rationale for this answer is as follows. A management decision, on the one hand, is the final stage of the management process aimed at finding and implementing the most effective solutions for the functioning and development of an organization, always accompanied by the development of alternative options for functioning and development. Depending on the specific goals, situations and problems of functioning and development, the process of developing ways (solutions) can be carried out in various ways. The typology of the management process (for example, a situational process that provides repeated clarification of the situation) may influence the nature and timing of the process of developing and selecting alternative solutions, but the management decision is also associated with the final choice of one of the alternative options. On the other hand, a management decision, like the choice of an alternative, is accompanied by a procedure for its adoption (there are also various ways acceptance - groups, decision makers, etc.), which includes the distribution of work between employees of the organization, the adoption of an action plan, the formulation of the task and organizational - practical work to achieve the set goals. Thus, the management decision as a choice of alternative determines the entire practical activities on the functioning and development of the organization.
Question 2. Why are there different approaches to defining the concept of “management decision”
Answer. Different approaches to defining the concept of “management decision” are associated with differences in the system of views and concepts of management, which were formed evolutionarily under the influence of changes in the management environment, the development of science, technology, production technology and management. Thus, at the beginning of the last century, management was based on the production paradigm, so management decisions depended on its results, on the provision of resources and their use to reduce production costs and increase profits. Transition to new paradigm management and broad human capabilities (in accordance with the scientific recommendations of behaviorism) expanded the range of management decisions and methods for their development, adoption and implementation.
Question 3. What stages of the management process constitute the necessary sequence of stages in the development of management decisions
Answer. The sequence of stages “goal - situation - problem - solution” reflects each of the various processes of developing management decisions. A management decision can be developed to achieve a set, adopted or adjusted goal (strategic, tactical, operational). Often the goal-setting stage requires repeated passage of this sequence of stages (the goal must be specific, measurable, controllable) and identified with the process of developing a management decision. Going through this sequence of stages reduces the role of negative manifestations of the properties of management processes (the properties of discreteness and inertia can lead away from the goal).
Question 4. What factors influence the typology of development of management decisions?
Answer. The environment plays a big role in shaping the types of development of management decisions. Certain changes in the external environment influence the choice of priorities in management tools, the role of managers, the types of motivation and form the type of management adequate to its changes. Thus, the transition to market relations intensified economic priorities, decentralized management, highly centralized management, and anti-crisis management. The management typology adopted in the organization also creates a corresponding typology for the development of management decisions. For example, with decentralized management, the development of management decisions is based on the principles of delegation of authority, and with anti-crisis management, it is based on the depth and degree of development of the crisis. The existing typology of developing management decisions changes mainly under the influence of the internal environment.
Question 5. How are management processes and the development of management decisions related?
Answer. The processes of management and the development of management decisions are interdependent, constitute unity and form the dynamics of management. Interdependence determines all organizational, functional and interfunctional relationships of the organization. The management process uses many different processes for developing management decisions. Thus, only certain divisions can participate in the development of strategic decisions top level organization management; when developing tactical decisions - divisions producing a separate product (process management); when developing operational decisions - a separate division of the organization.
Question 6. What does a management decision depend on in the process of managing an organization?
Answer. The effectiveness of management largely depends on the adopted sequence of stages and procedures of the management process. Studies of the patterns and properties of management processes (the objective existence of time gaps and discreteness, inertia and the oscillatory nature of the stages and procedures of management processes) show that the use of the necessary sequence of stages and procedures of the management process increases the effectiveness of management decisions.
Question 7. Note the most significant connections between the development of management decisions and types of management
Answer. The type of management generates a sequence of stages in the development of management decisions and plays a significant role in the formation of its processes. The sequence itself is varied and depends on the type of management decisions. The creation of such diversity is ensured by the purpose and organizational structure of management, the manager’s ability to generate ideas and options for management decisions, changes in the external and internal environment in which the management process is carried out. These features may not have a significant impact on the type of management (for example, when developing management decisions on the restructuring of debt obligations under the application of the Federal Law “On Bankruptcy and Financial Recovery of an Enterprise”).
Question 8. What role do management functions play in the development of management decisions?
corporate organizational management leadership
Answer. The essence and diversity of management functions are important in the development of management decisions. General management functions give rise to a typology of management decisions (planning and organizational decisions, decisions on motivation and control of the implementation of management decisions). Special and specific functions create the information field for management decisions (decisions of marketing and sales departments) or the conditions for developing management decisions (planning departments systematize, generalize and use information to develop options for planning decisions). In general, the functions reflect the content of decisions and correspond to the required variety of management decisions. The process of developing and making management decisions is formed not only by the functions of management, but also by the powers that determine the degree of participation of department heads in this process.
Question 9. What is the relationship between management functions and management decisions
Answer. The most significant relationships between management functions and management decisions are determined in accordance with the classification of decisions according to the content of management activities. For example, a unit performing planning functions is a department strategic planning- develops options for plans, but choosing the best option, which constitutes a strategic decision, is the prerogative of top management. In the case when the plan developed by the strategic planning department is related to the objectives of reducing production costs, the process of developing options includes production units, performing the functions of manufacturing products, because they more accurately determine the boundaries of cost reduction. Such relationships also exist between management levels (which are determined by the corresponding management functions).
Question 10. What role does the external environment play in the development of management decisions by public authorities?
Answer. In a market economy (as opposed to a command-administrative economy), the functions of government bodies change significantly.
Legislative bodies create a favorable legal environment for the activities of organizations, executive bodies, in accordance with federal and municipal functions, can influence the development of enterprises in certain industries and areas of activity of organizations (for example, on the conditions of activity and strategic development of small enterprises in the field of consumer services for the population of a particular region, city ). In this case, the standard of living, the state of infrastructure and the adopted strategic directions for the development of the economy of the region or city can play the role of the external environment of the activities of organizations. Its condition influences the decisions of state and municipal government bodies, whose functions include creating favorable living conditions for the population of a certain territory and organizations.
Question 11. What role does the external environment play in the development of management decisions? commercial organizations
Answer. The goals of commercial organizations are related to the economic categories of their activities and, more often, to the profit of the organization. If conditions do not allow achieving the accepted goals, activities may be suspended. If environmental changes do not contribute to the achievement of business objectives, they can be taken into account further as specific experience. In this case, the external environment influences the development of strategic goals related to changes in the organization’s activities. The adopted strategic goals can affect the typology of management, affect the resolution of personnel issues, and the development of goals and objectives of individual divisions of the organization.
Question 12. What role does the internal environment play in the development of management decisions of commercial organizations
Answer. The internal environment of an organization is formed by its main components: goals, objectives, structure and personnel. Possible positive changes in goals and objectives ensure the development of the organization and influence future results. But often increased obligations require the introduction of fundamental changes in structure and personnel decisions. Thus, the depth of changes in the internal environment is always reflected in specific decisions and the process of making them.
Question 13. What properties of management processes have the most significant impact on the process of developing management decisions
Answer. The dynamics of communication between the managed and control subsystems is ensured by the process of development, adoption and implementation of management decisions. Adjustments to its character are made by types of management decisions. In the process of developing strategic decisions, the scarcity of time as a management resource is of greatest importance; when developing tactical decisions - the cyclical occurrence of problems, the nature of discreteness and unevenness of management influences; in the process of developing operational decisions - the oscillatory nature of management.
Question 14. What role does organizational structure play in the process of developing management decisions?
Answer. Organizational structure how the composition and interconnection of links in the organization’s management system is based on securing the rights, duties and responsibilities of departments and their managers. The authority to make management decisions in accordance with the principles of their delegation can be transferred to the appropriate level and management functions. The functional division of managerial labor, enshrined in the horizontal and vertical connections of the organizational structure, must also correspond to the content of decisions: vertical connections determine the sequence of managerial influences, horizontal connections are established between individual aspects of decisions and their implementation.
Question 15. What role do hierarchy and levels of management play in the process of developing management decisions?
Answer. The hierarchy (subordination) of the organization is formed on the basis of decentralization of management so that a complex management task is solved by several simpler ones (although the words “simpler” are used here as a generalization, since the division of managerial labor leads to the deepening and complexity of tasks and specific management functions). When separating management levels, the hierarchy of the organization becomes more complicated, duplicating functions and separate links may arise. Determining the rational number of functions, tasks, levels and links that realize the advantages of centralization and decentralization of management belongs to the art of management.
Question 16. What role does authority play in the process of developing management decisions?
Answer. Authority directly relates to the process of developing, making and implementing management decisions. More often, authority is associated with the right to make decisions (the sphere of development and adoption) and forget about responsibility for the decision made (the sphere of implementation of management decisions). The connection between the right and responsibility for decision-making, united by the category “authority,” allows you to use the right to make decisions on various tasks: dividing the organization’s common goals and objectives into component subgoals and subtasks, creating conditions for the implementation of leadership qualities, creating and removing restrictions in the entire development process , adoption and implementation of management decisions.
Question 17. What role do management goals play in the process of developing management decisions?
Answer. The management goal as the desired state of the organization and the results of its activities over a certain period of time has a special impact on the process of developing management decisions to achieve it. There are many ways to achieve goals. In this regard, the set goal initiates the development of alternative solutions, selection and adoption of the most rational ones from the point of view of specific conditions and existing restrictions. In an organization that is guided by the principles of goal management, the decomposition of goals (“tree of goals”) is used in the process of developing management decisions. At the same time, goals and appropriate decisions for achieving them are determined for each division, link and performer.
The hierarchy of goals is built in such a way that the overall goal is achieved “from the bottom up”: achieving the goals of the lower links creates a certain resource or means for achieving the goal and the higher link. Goals can be consistent, contradictory, unbalanced in time and resources, and play the role of restrictions or criteria in the process of developing alternative management decisions.
Question 18. What role does the management methodology adopted in the organization play in the process of developing management decisions?
Answer. Management of a modern organization uses methodology as generalized scientific knowledge about the structure, principles, methods and means of management, which allows one to predict, plan and implement the process of achieving set goals. The methodology of managing an organization shapes its philosophy and the principles of management itself, which are manifested in the development and adoption of management decisions.
Question 19. What role does the complexity of the problem being solved play in the process of developing management decisions?
Answer. The complexity of the problems being solved is generated by many reasons. These include inflated goals, resource limitations, lack of information or time to achieve goals, low professional level of employees, lack of motivation, and more. The effectiveness of solving complex problems directly depends on the degree of development and decision-making at each of the successive stages of this process.
Question 20. What role do they play in the process of developing management decisions? personal qualities head
Answer. The personality of a manager plays a big role in managing an organization and is manifested in his leadership position at all stages of the management process. At the goal-setting stage, the leader can focus on goals that will allow him to realize his goals. leadership position. When assessing a situation, identifying problems, developing alternatives and choosing a solution, personal interests and ambitions can also have a positive or negative impact. Leadership is an important factor in effective management, but, nevertheless, in the process of developing management decisions, the role of personal qualities is not dominant.
Question 21. What role does organizational culture play in the process of developing management decisions?
Answer. Organizational culture reflects social aspects and priorities in the management of the organization. With the strengthening of the role of personality and creativity in the integrated result of an organization’s activities, there arises a need to use individual qualities managers and the culture of management relations to improve the processes of developing management decisions. Organizational culture creates a favorable environment for the development and implementation of all types of solutions. The development of organizational culture in modern organizations (especially those that use the international division of labor) becomes the object of corporate management. A high level of development of organizational culture is achieved by combining the level of education, professional training, personal discipline, effective use accumulated experience of collective activity and objectification of the processes of developing management decisions. Thanks to the developed organizational culture the system of collecting, processing, systematizing and analyzing information is streamlined, a favorable background is created for solving complex problems, a favorable environment for making changes and additional motivation for implementing solutions.
Question 22. What role does the organizational and legal form play in the process of developing management decisions?
Answer. The organizational and legal form determines the legal status of the organization and the mechanisms for developing and making management decisions related to the distribution of profits, property restructuring and other areas regulated by relevant laws. Often the organizational and legal form becomes a certain limitation in the development of the organization. The processes of developing management decisions related to changes in the organizational and legal form are carried out in accordance with federal legislation, and in other cases management decisions are subordinated internal regulations organizations.
Option 2
Question 1. What role does the scale of the problem being solved play in the process of developing management decisions?
Answer. The scale of the problem to be solved must correspond to the goals of the organization. Especially when management solves the problems of functioning and development of the organization. Development goals can create difficulties (temporary, in the use of scarce resources, conflicts of interest between managers and owners, etc.) in the implementation of standard and traditional tasks. To ensure that the scale of the tasks being solved does not destroy the organization, in the processes of developing management decisions it is used system analysis scale of integrated tasks.
Question 2. What role do types and areas of activity play in the process of developing management decisions?
Answer. The processes for developing management decisions correspond to the established types of management processes of the organization and the approved directions of its activities. When setting new goals regarding restructuring, entering new markets, producing a new product, etc., focused on the implementation of specific areas of activity, as well as changes in the internal environment, innovations can be used and formed in the organization innovation processes development of management decisions.
Question 3. What role does information play in the process of developing management decisions?
Answer. A management decision is characterized by special management information that gives the right to manage resources to achieve set goals. In the process of developing solutions, the information received is detailed, aggregated and converted into other information used to implement the solution in departments and performers. The process of developing decisions requires standardization of information and the use of a universal language (order, written or oral instructions). Despite wide range information resources, most management decisions (about 90%) are developed under conditions of uncertainty and their unification. Information plays a significant role in the formation of a certain understanding of processes, phenomena, objects and is used in the development of solutions as a methodological tool. Modern information tools expand management capabilities and increase the efficiency of the processes for developing management decisions.
Question 4. What role do the adopted long-term goals of the organization play in the process of developing management decisions?
Answer. Long-term goals drive the development of strategic decisions. The process of their development is characterized by a sequence of stages in which a special role is given to the development of a strategy, a strategic plan and the actual development of strategic decisions for its implementation. These types of activities use strategic management methods, but the development process can be different: targeted, branched or corrective.
Question 5. What role does production and its technology play in the process of developing management decisions?
Answer. Modern management has at its disposal a wide arsenal of methodological and methodological tools for developing management decisions. The development of typology and production technology influenced the range of decisions that expand or deepen the content of management activities. Therefore, the processes of developing management decisions are carried out in accordance with the main factors of production.
Question 6. What role does organizational structure play in the process of developing management decisions?
Answer. In modern management, the organizational structure as the interconnection of links in the organization's management system forms the basis for creating an effective decision development process. In different organizations, when using a standard organizational structure, different types of processes for developing management decisions may be used. A special role is played by the national and historical characteristics of management. They are manifested in the dynamics of management (in the development of decisions that require negotiation process, approval of changes, etc.), reflecting the features of the solution development processes.
Question 7. What role does legal support for managing an organization play in the process of developing management decisions?
Answer. Rights, duties and responsibilities for making management decisions are reflected in the organization’s charter, regulations on the enterprise, division (in accordance with the law, organizationally - legal form and field of activity). The use of appropriate documents ensures the legitimacy of the process of developing management decisions. Responsibility for the consequences of decisions made is assigned to the subject of the decision.
Question 8. What process of developing management decisions is determined by the linear organizational structure
Answer. A linear organizational structure is typical for small businesses. The management vertical is identified with a highly centralized solution development process. However, it does not always ensure the sequence of stages in the decision-making process and causes increased duration and gaps in the process of “development - adoption - implementation of decisions”, is characterized by the priority of authoritarian methods of decision-making and requires constant adjustment in the face of change.
Question 9. What process of developing management decisions is determined by the functional organizational structure
Answer. A functional organizational structure that uses a functional division of labor to separate functional units needs to develop goals and objectives for each unit and mechanisms for their coordination in the face of change. To ensure consistency and reduce the length of the solution development process, additional steps for evaluating and adjusting solutions are included.
Question 10. What process of developing management decisions is determined by the linear functional organizational structure
Answer. A linear-functional organizational structure uses the advantages of a linear and functional management organization. The process of developing management decisions depends on their type. They highlight decisions that are the prerogative of top management (strategic, personnel, financial, etc.); other decisions are developed and made in accordance with a branched type, determined by a variety of goals from the tasks of linear and functional units. Depending on the role and leadership qualities of managers, the process of developing and making management decisions can be decentralized (typical when separate divisions are separated into an independent legal entity), with the transfer of part of the decision-making powers to decentralized divisions. In this case, in the context of changes in the external environment, the process of developing management decisions to achieve the goals of the entire organization needs to be adjusted (for example, the development of strategic decisions using a corrective type).
Question 11. What process of developing management decisions is determined by the corporate management structure
Answer. Corporate management has become a special type of organization management (formed by independent legal entities) largely due to the development features corporate solutions. The development process includes procedures for collegial decision-making. At the level of organizations included in the corporation, the adopted collegial decisions are binding and determine the principles and areas of corporate activity. Established processes can be used to develop management decisions within each organization.
Question 12. What problems in developing management decisions arise in complex hierarchical management structures
Answer. In complex hierarchical management structures (management of an industry, a diversified complex, a regional economy, etc.), as a rule, the sequence of stages and the parallelism of problem solving are difficult. To prevent these difficulties, coordination of goals and resources, coordination procedures are used various types processes for developing solutions (characteristic of the specific activities of organizations in the field of education, culture, science, art, etc.), the relationship of decision makers. And the benefits of decentralizing decision-making.
Question 13. What is meant by the category “managerial decision making”
Answer. The essence of the category “managerial decision making” is associated with the procedure established in the organization for making management decisions in accordance with the responsibility and power of the decision maker. Traditionally, decision makers include line managers. In a corporation, some decisions can be made by the board of directors.
Question 14. How are the processes of “development of management decisions” and “making management decisions” related?
Answer. Making management decisions is no less a complex stage of management than its development. In decision development processes, including the development and selection of options, the adoption of a management decision, as the choice of an alternative, is considered the last stage of the process of its development. For spontaneous decisions, characteristic of authoritarian management, development and adoption can be combined into a single process. In functional departments, alternative solutions are developed, and the decision-making process (selection and decision-making) is assigned to a senior manager.
Question 15. What factors have the most significant impact on the management decision-making process?
Answer. Modern organizations can use the theory and experience of effective management in shaping management decision-making processes. In centralized organizations, due to the high responsibility of officials, this process is enshrined in legal and regulatory documents regulating the rights and responsibilities of the manager. In decentralized organizations (corporations), organizational behavior and decision-making principles play an important role, which can be adjusted in accordance with changes in goals, situations and the operating environment.
Question 16. What role does the behavior of managers play in the process of making management decisions?
Answer. The behavior of managers can influence the effectiveness of the decision-making process, but only when the situation or conditions of adoption require acceleration, decentralization or coordination of the decision implementation process. Thus, the authoritarian style increases the effectiveness of decisions made in conditions of concentrated responsibility of the decision maker; democratic style increases the efficiency of decisions made in conditions of effective decentralization; corporate style increases the effectiveness of decisions made in an active corporate culture. In general, the behavior of managers should not exert pressure on the decision-making process.
Question 17. What role do the personal qualities of a leader play in the process of making management decisions?
Answer. Personal qualities and leadership are the main components of the management potential of an organization. They play a vital role at all stages of development, adoption and implementation of management decisions. In practice, personal qualities play a big role in the processes of making management decisions in small organizations and groups. As an organization grows, organizational behavior, guided by corporate or other codes, plays a more significant role.
Question 18. What role does centralization and decentralization of functions play in the process of making management decisions?
Answer. Centralization and decentralization of management functions must correspond to the organizational structure, typology of management processes and development of management decisions. Centralization ensures the unity of management decisions, and decentralization requires coordination of functions and decisions. Ensuring the unity of management decisions in a decentralized management system is a necessary, but not sufficient condition for the decentralization of decision-making.
Question 19. What methods of developing management decisions are used in the process of implementing the plan?
Answer. When an organization's activity plan is developed and adopted (for example, a budget), administrative methods for developing management decisions are used in its implementation. Such processes are typical for the activities of dependent companies and subsidiaries. The plan development process includes the stages of backcasting, forecasting, organizational modeling and organizational design.
Question 20. What methods are used in developing a strategic plan for the development of an organization?
Answer. The development of a strategic plan is preceded by the development of an organization's strategy, depending on the content and type of strategy (related to the time interval - 3.5 or 10 years with the nature of changes in the organization's operating environment). But in the context of the adopted strategy, it is necessary to use strategic planning methods to develop a strategic development plan.
Question 21. When developing a strategic management decision, is it possible to limit ourselves only to quantitative information?
Answer. When developing a strategic management decision, both quantitative and qualitative information play an equally important role. Since quantitative information is calculated under conditions of risk and uncertainty, it cannot be comprehensive or reliable. Qualitative information makes it possible to assess the role of significant factors and their impact on changing the situation. Thus, one cannot limit oneself only to quantitative information when developing a strategic decision, since this limitation increases the risk of the decision.
Question 22. At what stage of developing management decisions are experts used?
Answer. Expert information can be used in the processes of developing management decisions. The stage at which the labor of experts is most effectively used is determined by the type of management decision. Thus, when developing strategic decisions, expert information will be required at the stage of assessing the situation, when developing tactical decisions - at the stage of identifying problems.
3. Option
Question 1. At what stage of the management process is the generation of management decision options used?
Answer. It is recommended to generate management decision options at the “decision” stage, when for each aspect of the decision under conditions of changing constraints (resources, prices, etc.), the consequences of making these decision options are taken into account. In the process of generating options, methods of group development of solutions are used.
Question 2. What contributes to an adequate understanding of the situation that can influence the decision?
Answer. Experiences of leaving (both negative and positive) from crisis situations develops a sense of the aggravation of the situation and adequate behavior of the manager. An experienced manager uses systemic and situational analysis more effectively and makes fewer mistakes in the decision-making process.
Question 3. What to consider when comparing alternative solutions
Answer. Determining the role of influencing factors when comparing decision alternatives is an important analytical activity. Practice shows that it is important to take into account the strengths and weaknesses of alternatives and plans for their implementation. Weak side There may be insufficient or exaggerated motivation of performers, changes in prices for resources in conditions of high costs.
Question 4. What methods of generating solution options are most used in any organization
Answer. Practice shows that the process of generating options is directly dependent on the type of decisions. Thus, to develop a new product in order to preserve confidential information, brainstorming methods are often used with the involvement of organization employees. In modern Russian organizations Marketing methods have become more widespread.
Question 5. Is it advisable to exchange information between experts during the examination process?
Answer. No, we need independent opinions.
Question 6. What is the difference between collective decision-making and collective expertise?
Answer. These are different processes. Collective decision-making (for example, in a board of directors, a meeting of shareholders, etc.) may require an examination of one or another decision option from the standpoint of reliability, effectiveness, consequences of adoption and implementation.
Question 7. Can an important management decision be developed without expertise?
Answer. Much depends on the type of management decision. IN effective management there are no unimportant decisions. In practice, important management decisions are developed in secrecy; expertise is used only to assess the situation characterizing the real state of affairs.
Question 8. What decisions link strategic and tactical goals
Answer. Consistent achievement of tactical goals ensures the achievement of strategic goals. The alignment of tactical and strategic goals must be reflected in the strategy implementation plan (moving up the stairs, it is dangerous to jump over the steps!).
Question 9. Who has the greatest influence on the formation of the organization’s goals
Answer. In a market economy, the consumer becomes at the center of the processes of developing management decisions; it is with him that the goals of the organization are associated.
Question 10. What is the role of resources in adoption? long term plans organization development
Answer. Resources ensure the achievement of all goals, including the development goals of the organization.
Question 11. What methods of goal formation are used in practice?
Answer. In practice, in a competitive environment, the formation of goals is carried out by a narrow circle of people or an initiative group of employees of the organization.
Question 12. What role does the “tree of goals” play in the development of management decisions
Answer. The “Tree of Goals” allows you to determine the range of tasks and solutions for departments and specific performers, and subsequently the planning and coordination of the work of departments and performers is carried out.
Question 13. What role does the organization’s mission play in the development of management decisions?
Answer. An organization's mission is developed when an organization wants to determine its social significance and position its activities or product production. Thus, the mission allows you to control development directions and develop solutions within the approved areas of activity.
Question 14. What role does the value system play in the development of management decisions?
Answer. In the processes of developing management decisions, they rely only on those values that are reflected in the mission of the organization.
Question 15. What role do competing goals play in the development of management decisions?
Answer. Competition of goals, as a rule, leads to conflict of goals and social conflict between departments or individual performers. The conflict resolution process often leads to a reassessment of the goals set.
Question 16. What role does monitoring play in the development of management decisions?
Answer. Provides information for decision making under conditions of uncertainty.
Question 17. Why is it necessary to monitor the internal external environment of an organization to develop management decisions?
Answer. Depending on the type of management decision, in the process of its development, information about the state of the external (strategic and tactical decisions) and internal environment (operational decisions) is used. IN competitive environment information about environmental changes can be critical. In this regard, monitoring allows you to adequately respond to changing situations.
Question 18. How are management decisions measured?
Answer. Measuring management decisions is difficult; most often this measurement concerns the economic and social consequences of making and implementing management decisions. In practice, assessment is carried out using quantitative and qualitative indicators of the effectiveness of the solution.
Question 19. Why are management decisions measured using quantitative and qualitative indicators?
Answer. This is due to the fact that the goals of organizations and its divisions are formulated using quantitative and qualitative indicators.
Question 20. What criteria for measuring decisions are most often used in practice?
Answer. In practice, the results of the organization as a whole are used as criteria for measuring management decisions, and recently the quality of the product produced and sold has been used as the most important criterion.
Question 21. Why are different management models formed? different systems decision evaluations
Answer. The formation of a management model is influenced by methods for developing solutions. The variety of methods determines the development various systems evaluation of management decisions. The use of a specific set of solution development methods forms the technology for developing, making and implementing decisions. At the same time, decision evaluation is included as a system element of the technology and management model.
Question 22. What is the relationship between the criteria of effectiveness and efficiency of decisions
Answer. Productivity is related to labor productivity, efficiency is related to economic results obtained over a certain period of time.
4. Option
Question 1. What role does professional preparedness play in the development of management decisions?
Answer. Professional preparedness improves the quality of developed management decisions.
Question 2. What methods of measuring management decisions are most common in Russian management practice?
Answer. In Russian practice, management decisions are measured by the economic results obtained in the process of implementing the decision.
Question 3. What are the connections between the measures of management decisions and the effectiveness of the management system as a whole?
Answer. The connections between decisions and organizational performance can be monitored through a system of economic indicators.
Question 4. How can we define the “space of effective solutions”
Answer. This is a space formed by goals, knowledge (information) and the effectiveness of the decision.
Question 5. What role does information influence play in the development of management decisions?
Answer. Information impact can stimulate development, appeal to interest, or radically change the attitude towards the solution being developed.
Question 6. How is the basic information of management decisions formed?
Answer. It is formed gradually and accumulates in databases.
Question 7... What role does information power play in the development of management decisions?
Answer. Information power influences the distribution of tasks in the organizational management structure.
Question 8. How, by analyzing the process of developing management decisions, can you determine the degree of interconnectedness of the links of the management system
Answer. It is recommended to include managers of the decision implementation process in the process of developing management decisions. Analysis of the interconnectedness of their goals allows us to determine at the early stages the degree of interconnectedness of the included (and not included) links of the management system.
Question 9. What sources of information affect reliability and completeness information base management decisions
Answer. The information and documentation system of the organization serves as the information base for management decisions. For many management decisions this base is not enough. Constant replenishment and updating of the information base is required. At the same time, it is important to know that no source of information is immune from unreliable information.
Question 10. What functions form the cycle of development of management decisions
Answer. The basis of the development cycle of management decisions is made up of general management functions: planning, organization, motivation, control.
Question 11. How does aggregation and disaggregation of the functions of the management decision development cycle affect the implementation of its individual stages?
Answer. Aggregation and disaggregation should be carried out taking into account their effectiveness.
Question 12. How are goals, decisions and their agreement developed?
Answer. Using a systematic approach and a “tree of goals”.
Answer. This is a sequence of stages, algorithms and operations in the process of developing management decisions.
Question 14. What problems for the development of management decisions are created by the complication of connections between divisions of the organization
Answer. The decision control system is becoming more complex.
Question 15. What role does the span of control play in the processes of developing management decisions?
Answer. The higher the range of control, the more the nature of the activity and the professionalism of the performers must be taken into account.
Question 16. What role does centralization of management play in the processes of developing management decisions?
Answer. Narrows the field of alternatives.
Question 17. What role does decentralization of management play in the processes of developing management decisions?
Answer. Expands the scope of alternatives.
Question 18. What role does delegation of authority play in the processes of developing management decisions?
Answer. Increases responsibility for solution development.
Question 19. What role does compliance with the principles of delegation of authority play in the processes of developing management decisions?
Answer. Contributes to the efficiency of solution development.
Question 20. What role does integral responsibility play in the processes of developing management decisions?
Answer. The development of the organization is associated with the expansion of production, innovation in the field of production and management, expansion and deepening of the market and restructuring. At the same time, separate divisions (with high independence in management) may appear in the organization, carrying out the process of supply, production, sales, innovation or research activities. For such units, conditions for integral responsibility are being developed. They increase the efficiency of the solutions being developed (in the department and the organization as a whole).
Question 21. What principles of delegation of authority are implemented in the processes of developing management decisions
Answer. In practice, the principle of functional definition and the principle of level of authority are used. The principle of functional definition allows you to develop a solution in accordance with the fixed functions, the principle of the level of authority determines the rational level of responsibility for making and implementing a management decision.
Question 22. What role does research play in the processes of developing management decisions?
Answer. It depends on the type of decision, but in general, research is used at each stage of developing management decisions.
5. Option
Question 1. What organizational changes need to be made when implementing the marketing concept for developing management decisions
Answer. It is necessary to make an organizational and psychological transition to the implementation of the marketing concept.
Question 2. What problems does Russian management face in developing marketing solutions?
Answer. Modern Russian management widely uses marketing theory, but loses effectiveness due to inappropriate consumer behavior.
Question 3. What is the quality of a management decision?
Answer. The effectiveness of management depends on many factors. One of these factors is the quality of management decisions. The category “quality” has several interpretations. They are used to characterize resources, manufactured products, and management processes. The quality of a management decision represents a set of properties of the decision that make it possible to obtain the effect of its implementation.
Question 4. How is the quality of management decisions assessed?
Answer. To assess the quality of a management decision, indicators such as development and implementation time (just in time), social and economic indicators are used, which make it possible to assess the future results and consequences of the solution being developed. In practice, the quality of a management decision is associated with the result and consequences of its implementation.
Question 5: What role do standards play in developing product quality decisions?
Answer. Product quality is not only a result of production. In modern management, quality is formed in the management of the organization. In this regard, quality standards (especially international standards) make it possible to determine the procedure and methods for planning to improve product quality at all stages of the life cycle.
Question 6. What factors influence the quality of management decisions
Answer. The quality of management decisions is influenced by many factors. The most important ones include professionalism, experience, production and management technology, and demand for product quality. In order to take them into account, quality divisions are formed in organizations, the functions of which include collecting, processing and systematizing information about product quality, planning the quality level, etc. (such divisions are formed in many educational institutions). In order for quality departments to work effectively, it is necessary that the organizational structure and the technology adopted in the organization for developing and making management decisions include an assessment of the influence of quality factors.
Question 7. How to measure the effectiveness of management decisions
Answer. In modern management, depending on the types of management decisions, different methods of measuring efficiency are used. The most common and adequate way of measurement is to assess the degree of compliance and achievement of the set goals (performer, department and organization as a whole). At the same time, depending on the level and hierarchy of management decisions, an appropriate system of social and economic indicators is used.
Question 8. What indicators of the effectiveness of management decisions are used for assessment in state and municipal authorities
Answer. In practice, assessment of the effectiveness of government bodies is often associated with the personnel heading the relevant departments. But such approaches to assessment are insufficient. In accordance with the functions and powers of legislative and executive bodies and the level of government (federal, constituent entities of the Russian Federation and municipal bodies), indicators of socio-economic development of the subordinate territory are determined. They are used to assess the effectiveness of territory management.
Question 9. Why does economic justification occupy a special place in the system of comprehensive justification of management decisions?
Answer. In market relations, the economy is the most important factor development of a person, family, organization, territory. Economic indicators that reflect the interests of the owner of the organization, consumers, local community, and the state act as restrictions in the assessment and selection of alternative paths and solutions. The criteria for choosing alternatives are also primarily of an economic nature. In this regard, economic justification is a systemic element of a comprehensive justification of management decisions in organizations of any organizational and legal form.
Question 10. What aspects of management are not considered when economic justification management decision
Answer. In management, the personal qualities of a leader play an important role. But the peculiarities of the relationship between managers and performers are not the object economic assessment. It is believed that relationships should facilitate the implementation of management decisions.
Question 11. What situations have a significant impact on the process of achieving the goal?
Answer. The process of achieving a goal is accompanied by changes in the organization's operating environment. Some changes are predicted (predictable situation), others may arise spontaneously as a result of systemic connections between several factors (unpredictable situation). The immediate impact of unpredictable changes on supply, production and sales brings the greatest costs. Such situations include the emergence of a shortage of products and resources.
Question 12. Choose the best criterion for determining product shortages
Answer. Increase in the number of orders for products.
Question 13. How to determine the shortage of raw materials and materials
...Similar documents
Management: concept and essence. Motivation theory. External environment organizations. Organizational management structure. Communication process, its elements and stages. general characteristics management functions. Management decisions. Personnel management system.
lecture, added 12/18/2008
Management decision as a choice of alternative in the process of implementing the main functions of management, features and differences between management decisions and other types of decisions. Factors influencing the quality of management decisions, the essence of uncertainty.
course of lectures, added 05/05/2009
Functions of management decisions in the management system. Ensuring progress towards the goals set for the organization. Encouraging enterprise personnel to achieve the goals set for employees. Official powers and responsibilities of the manager.
presentation, added 12/08/2014
Principles of strategic management. Managerial decisions in the selection of strategic alternatives. Quality like economic category and control object. Documentation of the quality management system. Quality assurance cost management.
thesis, added 12/01/2008
Basic approaches to making management decisions, its effectiveness, methods of adoption and functions, technologies and models. Decisions of the highest level of management, forecast alternatives, taken in the prescribed manner and having mandatory significance.
course work, added 11/07/2014
The essence of leadership and approaches to its study. Basic qualities needed for a leader. Organizational management structure and leadership style in the organization. Combating imperfections in personnel management functions. Increasing the efficiency of personnel policy.
course work, added 04/08/2015
Consideration of deterministic and probabilistic management decisions. The sequence of stages of making a management decision, its role in the management system. Assignment of discount factor. Estimation of the mathematical expectation of possible income.
course work, added 09/22/2015
Type classification of organization management as the interaction of an object and a subject. The essence and structure of management (management). Solutions management tasks. Features of financial and trade management. Communications as an element of the management system.
abstract, added 01/11/2012
The essence, characteristic features of a management decision and its role in the management system. Analysis of the external and internal environment of Ufa Crane Manufacturing Plant LLC. Conditions and factors for the quality of management decisions, recommendations for its improvement.
course work, added 06/03/2011
The essence and content of the main management functions, criteria for their classification and place in the management system. The role of management functions in the formation of management structure. Improving the application of management functions in a municipal organization.