Can a working person open an individual enterprise? How to open an individual entrepreneur - instructions and necessary documents Can I work and open an individual entrepreneur
In search of additional income, many people wonder if it is possible if you work officially. The answer is ambiguous. In addition, it has several aspects of a legal, organizational and psychological nature. Here are just some of them:
- whether the employee has enough strength and time to engage in entrepreneurial activity along with his main job;
- how beneficial is such a combination;
- whether the employer may become aware of such a combination, and how he will react if he finds out.
Is it possible to open an individual entrepreneur for a working person: restrictions?
What are the obstacles to opening an individual entrepreneur for a working citizen?
- Lack of full legal capacity. First of all, this is a question of age (you can work under an employment contract from the age of 16, but engage in entrepreneurial activity only from the age of 18). You can get around this restriction by getting married or going through the emancipation procedure.
Secondly, we are talking about a court decision declaring a person incompetent or partially capable. Incapacitated citizens are not able to work for hire, requiring constant supervision. But persons whose legal capacity has been limited by the court due to alcohol and drug abuse, as well as gambling addicts, can work, but cannot engage in business until the court restores full legal capacity.
- Establishment of special restrictions in a court sentence in connection with the commission of official or property crimes.
- An absolute ban on combining primary activities with business activities has traditionally been established for persons in public (state or municipal) service.
- Similar legislative restrictions are defined for persons engaged in specific types of individual activities - lawyers, notaries.
Is it possible to register as an individual entrepreneur and combine work officially with some types of employment?
- Staying in an elected position.
The following cannot engage in entrepreneurial activity:
- deputies of the State Duma of the Russian Federation;
- heads of municipalities;
- deputies of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation and deputies of all levels performing duties on a permanent basis (deputies, deputy chairmen, secretaries).
The rest of the deputies are allowed to do this.
- Lack of Russian citizenship. Citizens of other states and stateless persons can engage in entrepreneurial activity only with the permission of the Federal Migration Service.
Entrepreneur-public sector employee, entrepreneur-civil servant: is this possible?
Can a civil servant open a sole proprietorship if he is employed in a state-owned institution? Many people mistakenly believe that yes, confusing the concepts of “employee” and “civil servant.” Let's look at an example.
A school teacher is not a civil servant. Therefore, he may have a private practice as a tutor or tutor. At the same time, a teacher - an employee of the local education department, being a civil servant, is limited in such activities.
Similarly, a physician employed in a hospital can simultaneously be an entrepreneur, but an employee of the territorial body of Roszdravnadzor cannot.
How does registration of entrepreneurial activity affect labor relations?
Actually nothing. But at the same time, the question arises: can an individual entrepreneur? After registering as an entrepreneur, a person continues to receive a salary, and there are deductions to the Pension and other funds. He has no new obligations.
Since only records of work for hire are made (Article 66 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the fact of registration and termination of entrepreneurial activity is not recorded there.
Thus, these two separate systems - entrepreneurial activity and hired labor - do not intersect in any way: the calculation of taxes and the calculation of length of service are carried out separately by the employer and the entrepreneur.
An employer can find out that an employee is an entrepreneur only by chance, by seeing a business card or by stumbling upon it. This issue cannot be clarified when submitting reports or similar procedures.
Information about persons registered as individual entrepreneurs is contained in a special register of the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs maintained by the tax service. To obtain data, you must formally submit an application, pay the appropriate amount and wait for a response.
Each person sees success in their own way. While some of us are building a career step by step, others are striving to open, albeit small, their own business. However, business is always fraught with risk, and few people are ready to leave a job with a stable income before starting this path. How does being an entrepreneur compare to being an employee? In other words, is it possible to open an individual entrepreneur if you are officially employed?
Entrepreneur status
An individual entrepreneur (IP) is not an organizational and legal form of a small enterprise, but a special status of an individual. It provides a legal basis for doing business and making a profit, and also imposes a number of responsibilities: pay taxes and insurance contributions, report to government agencies, and bear responsibility for your obligations. However, having registered as an individual entrepreneur, a person does not cease to be an ordinary citizen with his inherent rights and responsibilities. Including the right to be hired.
In other words, the statuses of individual entrepreneurs and employees most often do not intersect with each other and get along well. Therefore, the question “is it possible to open an individual entrepreneur if you are officially employed” generally has a positive answer, although with some reservations, which will be discussed below.
Who can and cannot be an entrepreneur
A person who intends to engage in entrepreneurial activity must meet the following requirements:
- have Russian citizenship;
- belong to the age category of 18 years or more (while working for hire is allowed from the age of 16);
- be fully capable, that is, do not have a limitation of legal capacity that can be established by a court decision in relation to persons with mental disorders or addicted to alcohol, drugs or gambling (such persons can work for hire, but cannot be individual entrepreneurs);
- have no judicial, professional or official restrictions on conducting business activities.
An entrepreneur carries out his activities at his own peril and risk, and this must be clearly understood. That is why the individual entrepreneur must be an adult and fully capable person who can be held responsible for his actions.

Professional and job restrictions
Sometimes a person’s position or profession may indeed make it impossible to register an individual entrepreneur, but such cases are few. Thus, it is prohibited for state and municipal employees to act as an entrepreneur. The ban was introduced in order to ensure that they can effectively carry out their work without being distracted by other activities. In addition, it is designed to eliminate the possibility of civil servants using their privileges in the course of developing their own business.
In connection with the above, the question arises: “Is it possible to open an individual entrepreneur if you are officially employed in a government agency?” In most cases, it is possible, since working in such organizations is not a civil service by default. The list of civil service positions is established by presidential decree, as well as by acts of the constituent entities of the Federation. If you have any doubts about whether your position belongs to the civil service or not, you should turn to the legislation and find out this question.
A separate professional category, representatives of which are not able to register individual entrepreneurs, are notaries and lawyers. Like entrepreneurs, they conduct individual activities, pay taxes and submit reports themselves. However, their activities are not entrepreneurial, since their main goal is not to make a profit.
Also, for ethical reasons, the law prohibits heads of municipalities, deputies of the State Duma, Federal Assembly and some other categories of deputies from registering as individual entrepreneurs.
What does a future entrepreneur need to know?
So, we have covered in detail the question of whether it is possible to open an individual entrepreneur if you are officially employed. But this is far from the only thing that a future businessman should think about. Many people mistakenly believe that the status of an entrepreneur does not oblige you to anything: if things go well, good; Well, if not, then there is no demand! But this is by no means true. Registering as an individual entrepreneur and forgetting about it “until better times” will not work, and here’s why.
Regardless of whether the activity generates income or not, the individual entrepreneur must make contributions to insurance funds: pension (PF) and medical (MHIF). Contributions are payable even if no business activity is carried out at all. That is, your business is still in its infancy, and insurance deductions must already be made in full! Now their total amount is about 20 thousand rubles per year, and this amount is slowly but surely increasing.

In addition, even with zero activity, it is necessary to submit reports to the tax office (IFTS). Failure to comply with this requirement, as well as violation of established deadlines, entails a fine.
There is another key point in the activities of an entrepreneur - he is responsible for his obligations with all his property. That is, unpaid insurance premiums, taxes, fines, as well as any loans, borrowings and other obligations arising within the framework of business activities are personal debts of an individual. And the collection of these debts can be carried out at the expense of the property belonging to the person.
Is it worth the risk?
Doubts about whether it is worth opening an individual entrepreneur if you work officially arise for another reason. A person is simply not sure that he can successfully combine work and entrepreneurial activities. Business development is a difficult matter, and no one guarantees success. The main work also requires a lot of effort and time. Even if everything is carefully calculated, there is always a chance of encountering unforeseen difficulties, the solution of which will require more resources than planned. Therefore, before opening an individual entrepreneur, it is worth considering whether there will be an economic benefit from such a combination. After all, everyone knows what happens when you try to keep up with two birds with one stone...

What is better - being hired or having your own business? Everyone must answer this question for themselves. For those who have decided to try themselves as an entrepreneur, we will next tell you about the registration process.
Collection of documents
Registering as an entrepreneur is a fairly simple process. Documents for opening an individual entrepreneur are presented in the following list:
- passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation;
- certificate of assignment of a TIN (if not available, you must obtain it from the regional Federal Tax Service);
- application in form P21001;
- paid state duty in the amount of 800 rubles (original and copy of receipt);
- 2 copies of the notice of transition to the simplified taxation system - a simplified taxation system (if absent, it is assumed that the individual entrepreneur will apply the general taxation regime).
You need to think about choosing a tax regime even before opening an individual entrepreneur. Most entrepreneurs prefer the simplified tax system, since under this regime there is no need to keep accounts, as well as pay VAT, income and property taxes. Accounting is reduced to filling out a book of purchases and sales, and all taxes are replaced by one, which is calculated at a rate of 6% of income or 15% of profit (optional). It is also worth considering that some types of activities fall under other taxation systems - EVND, patent or Unified Agricultural Tax. There are often situations when an individual entrepreneur is forced to apply several tax regimes at once.

Registration process
Registration of individual entrepreneurs is carried out in the territorial bodies of the Federal Tax Service. The set of documents can be taken there in person, transferred through a representative authorized by a notarized power of attorney, or sent by mail in a valuable letter. In the last two cases, form P21001 must be certified by a notary. Also, documents can be submitted for registration to the nearest MFC (multifunctional center of public services), however, not all service branches yet provide this opportunity.
After three working days, the documents will be ready. To confirm that business activities can now be carried out legally, you will receive a registration certificate and an extract from the register of individual entrepreneurs. Along with these documents, you will be returned one copy of the notice of application of the simplified tax system, containing a mark from the Federal Tax Service. Well, that's all, you have become an individual entrepreneur!

Information about the new individual entrepreneur is transferred from the tax service to the Pension Fund, where a registration number is assigned. Notification of registration with the Pension Fund along with a memo from the payer of insurance premiums will be sent to you by mail. In the meantime, you can order a print and, if necessary, open a bank account.
This completes the process of registering an entrepreneur; it’s time to start developing your business! And, of course, it is important to make mandatory payments on time, as well as submit reports to regulatory authorities.
Business and work can be combined, since there are many positions that provide the opportunity to earn money and at the same time allow you to develop your own business. On the other hand, if you have free time, you can start your own business and earn additional income. But in practice, not every field of activity allows you to get a certain position and open an individual entrepreneur at the same time. Let's consider these aspects in more detail.
Opportunities for opening an individual entrepreneur: legislative acts
Registering as an individual entrepreneur today is not particularly difficult, and many opportunities open up for promising individuals full of strength, energy and ideas. But no one can guarantee the successful implementation of a business project, so there is a desire to insure oneself against financial losses.
Recommended: Successful businessmen advise beginners at the start of organizing their own business to leave the possibility of another stable source of income, so that in case of failure they will have the means to lead a normal life.
The question arises: is it possible to obtain the status of an individual entrepreneur without resigning? Let us turn to the regulations and the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
- Article 18 states that every citizen who wishes can conduct business activities that are not prohibited by law. In this case, such a person must reach the age of majority and have civil rights.
- Article 23 indicates that a person receives the right to do business from the moment he receives the status of an individual entrepreneur.
- The Law of the Russian Federation “On Registration of Individuals and Legal Entities” states that there are no prohibitions on such actions.
These regulations indicate that it is possible to combine activities under an employment contract and at the same time be a registered individual entrepreneur. However, there are limitations and exceptions to such rules.
As people say: “there is never too much money.” So, for many promising people, this phrase is simply a motto in life. And as practice shows, such people have one, two, or even three jobs, and at the same time, they additionally dream of opening their own business.
This is a pretty good idea, since having several jobs, initial capital for the business will not be a problem, and even in case of failure, there will not be any significant losses.
But, there is one catch, which lies in the question: “is it possible to open an individual entrepreneur if you are officially employed?”
Is it possible to open an individual entrepreneur if you are officially employed?
Before attempting to open your own business, registering as a private enterprise, you should be well prepared, both morally and legally.
For example, the first nuance that you definitely need to know is that being an officially employed employee, you have a certain number of obligations to your management, as well as to the state.
Therefore, in case of failure to comply with them, for any reason, you will have to answer to the court.
But this criterion relates more to the question of whether : Is it possible to work and be an individual entrepreneur at the same time? As for the prohibitions on the opening itself, the country’s legislation has a certain list of labor activities in which it is impossible to open an individual business.
The list of professions prohibited for individual entrepreneurs primarily includes all positions related to state or municipal service.
For example, these could be:
- lawyers;
- lawyers;
- notaries;
- employees of local or regional authorities;
- deputies (if they are citizens of their country. For persons with citizenship in another country and holding a similar position, the opportunity to register an individual entrepreneur on the territory of the Russian Federation remains valid).
This is due to the powers of the people working in the above structures, as well as the degree of their responsibility. When occupying high positions, you should treat your work professionally, devoting all your free time to it.
But, there are exceptions to this law. For example, the court, on an individual basis, may allow the opening of individual entrepreneurs to persons belonging to the state or municipal service. Also, in some cases, the judicial authority itself may decide to deprive the right to engage in individual entrepreneurship of those individuals whose professions are not included in the above list.
Returning to the question of whether it is possible to open an individual entrepreneur while working officially, it should be mentioned that the considered criterion is far from the only one for banning entrepreneurship.
In addition to certain officials, employees who do not have full legal capacity (that is, those under 18 years of age) cannot register as a sole proprietor.
Such cases are quite possible, since according to the law, it is officially permitted to work from the age of 16.
But this limitation can also be circumvented if desired.
To do this, you need to enter into an official marriage, or go through the emancipation procedure (renunciation of all factors on which you depend, including parental guardianship).
Both of these options provide for the complete end of all restrictions provided by the state for persons who have not reached full legal capacity (up to 18 years of age), and the acquisition of all full rights and obligations.
There is also a second side to the coin - if the incapacitated person is so not due to age, but as a result of a congenital disease or acquired injury. Such cases, of course, are not common, but they do occur in the practice of registering individual entrepreneurship.
Another criterion that undoubtedly imposes a ban on individual entrepreneurs is the presence of alcohol or drug addiction. That is, if you are registered with a narcologist due to repeated use of alcohol and drugs, then you can completely forget about such an idea. There are no exceptions in this case.
Well, the last criterion prohibiting individual entrepreneurship refers to the category of workers who are supported by the state. But, in this case, there is a certain fine line.
For example, private school teachers are not government employees and can easily do their own thing.
This practice is very common, and allows teachers to additionally engage in tutoring or paid consultations at home.
The same applies to medical workers. If a person is officially employed in a private clinic or hospital, then he has full right to an individual entrepreneur. And in the case when the same person works in the territorial body of Roszdravnadzor, there will be no opportunity to register an individual entrepreneurship.
How registration of an individual entrepreneur can affect working relationships
Returning to the question: “can an individual entrepreneur work at another job?”, it is necessary to make a firm conclusion - yes, he can. But what if you look at the situation from the other side, from the point of view of the question: “what will be the attitude towards you at your previous place of work?”
As practice shows, all managers and bosses are, first of all, concerned about how well the employee copes with his responsibilities, and the rest of your life aspects will be of little interest to him. Thus, if your business does not interfere with your main work and does not affect your ability to act, then the attitude of your superiors towards you will not change.
Of course, if you are an excellent specialist in something, and in the future, opening your own individual entrepreneur may affect your departure from your main job, then management will be somewhat concerned about this outcome of events. But, in most cases, such situations are treated adequately and with understanding.
It is also worth noting that, if you wish, the employer may not even know that you have an individual business. After all, data about this is recorded in only one place – the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs (USRIP). And you can obtain such information from this service only for a certain fee, by submitting an application in an official form.
As for the state, it will also not change its attitude towards you after registering an individual entrepreneur. You will still be able to receive well-deserved contributions to the pension fund, go on paid leave, and be financially insured in case of any injuries or illnesses at work.
In what cases should you register as an individual entrepreneur, and what advantages can this bring you?
We have already dealt with the question: “is it possible to open an individual entrepreneur if you are officially employed?”, and now we can move on to a more interesting question: “what privileges and prospects will open up to you in this case?”
The first thing you should pay attention to is the fact that individual entrepreneurship obliges a person to fill out business reports, and also, without fail, submit them to the appropriate authorities in a timely manner. In addition to reports, a certain amount of money must be paid monthly, which completely depends on the individually established tax system.
As practice shows, such events take a lot of time, which is already a small disadvantage for an entrepreneur with official employment. Therefore, you should carefully analyze: do you absolutely need an individual entrepreneur?
After all, the goal of any individual entrepreneurship is to open your own business, which, most often, is based on the sale of any category of goods, or the provision of any services. But in most cases, this can be done without the process of obtaining an individual entrepreneur.
For example, you can open your own online store, or create your own website on which you will provide certain services online. In principle, this is the same as a full-fledged business, but with much fewer requirements.
In general, individual entrepreneurship should be opened if you:
- you sell goods, not via the Internet. To sell any category of goods, a special certificate is required, which is issued only by government agencies. And without having an individual entrepreneur, this certificate will not be issued to you;
- Are you planning large-scale marketing? This includes not only advertising on the Internet, but also on television, in local newspapers, and even on billboards in your city;
- Do you want to make a terminal for card payments? Also, this device is capable of issuing a receipt about the operation performed, which is not unimportant in this case.
If you don’t need all this, then registering as an individual entrepreneur will also not be a mandatory criterion for you. Well, if, nevertheless, you have decided that entrepreneurship is an integral part of business, then let’s consider the option of obtaining it in more detail.
Today, the procedure for registering an individual entrepreneur is very simple and will not take a lot of your time and money. For example, in order to open a business, you do not have to rent an office or any other premises to register it, since your business will be registered at your place of residence.
When drawing up an application for an individual entrepreneur, you will be required to provide a minimum package of documents, which includes:
- passport;
- a receipt from the bank, which indicates payment of the mandatory state duty (today, no more than 800 rubles);
- the statement itself;
- in the case when the business is registered in the name of a trusted person, a special document (power of attorney) certified by a notary is required.
In terms of time, this procedure takes from one to two weeks, which is also a fairly short period of time.
Also, many are interested in one important question: can an individual entrepreneur work in another organization registered as a private entrepreneur? The answer is extremely simple: naturally it can.
In fact, any business that provides official places for employment is obliged to provide a full social package to its subordinates, regardless of whether he is an individual entrepreneur or not.
And even more so, as was previously said, the authorities do not need to know that a business has been registered in your name.
By the way, a big plus for an individual entrepreneur is that all items purchased for the business are registered in his name, and in the event of the closure of the business, they become his private property and are not sealed. Also, in many cases, when submitting reports, you do not need to have your own seal. This is very convenient, since you do not need to spend extra money and funds on its registration.
Disadvantages of individual entrepreneurs in official employment
The question is: “is it possible to open an individual entrepreneur if you work officially, and what are the benefits of this?” - we have already considered. Now, let's look at this situation from the other side - from the side of the shortcomings.
There are practically no significant disadvantages when opening an individual business, and to be precise, there is only one. Its essence is binding to the place of residence.
After all, you, as the head of your own business, are required to submit reports and revenue within a certain period of time, and only at the place of registration of the business.
And if you need to go on a business trip to another city, this circumstance may cause some difficulties.
Well, other disadvantages, such as: the inability to reduce the tax base, the reluctance of cooperation from other legal entities that are accustomed to working with JSC, etc., will not play a special role. After all, sooner or later, you will have your own turnover and your own customer base.
After reviewing the above information, we were able to answer the question: “is it possible to open an individual entrepreneur if you are officially employed?” Also, we were able to soberly and adequately assess all the pros and cons of entrepreneurship, weigh them, and determine the need for opening it. So, with the acquired skills, you are unlikely to encounter any pitfalls on the way to registering as an individual entrepreneur, because you are already well acquainted with this procedure.
Is it possible to open a sole proprietorship if you are officially employed?
The salary of a working person in most cases leaves much to be desired. In the worst case, the employee begins to look for additional means of earning money, and in the best case, he begins to open a business on his own.
It’s only when the desire for independent entrepreneurship appears that the question invariably arises: is it possible to open an individual entrepreneur if you are officially employed? No one can give a definite answer to this question, and its consideration must be comprehensive and multilateral.
What restrictions may there be?
The person who decides to combine work with private entrepreneurship must understand that this opportunity is not available to everyone. There are legislative prohibitions on private entrepreneurship, and if an employed person falls under them, then opening a private business in the form of individual entrepreneurship is not available to him.
The first such obstacle can be considered incapacity, which is confirmed by a court decision. It can be triggered by gaming, drug, or alcohol addiction. Actually, in this case, even ordinary employment is a very controversial issue, so the idea of entrepreneurship in this case is rarely relevant.
However, readers should know that the work of a private entrepreneur in the current situation is possible only after this person is recognized as legally competent.
Another obstacle to becoming an individual entrepreneur may be official employment in public or government positions. In this case, running a private business is prohibited by law.
The specifics of the activity (in the form of a lawyer or notary) will also be an obstacle to opening an individual entrepreneur.
Will the employer notice the individual entrepreneur?
Many employed people are concerned about how the employee’s employment in private enterprise will affect labor relations, as well as how management will react to this fact. It is worth saying that this question is irrelevant, since opening your own business entity does not imply entries in the work book or notification at the main place of work.
All data regarding a registered private entrepreneur will be stored in the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs in the tax authorities, and obtaining data from the register is only possible by contacting the tax office in the official format.
This means that an employer who wishes to obtain information about whether his employees are private entrepreneurs must contact the tax authorities with a corresponding application, pay a certain amount, and if the tax authorities decide to provide this information (which is unlikely), wait for the appropriate notification.
Things to think about
An employed person who has decided to create his own business entity should definitely weigh the pros and cons in order to avoid infringement of his activities, both private and at the place of employment. Entrepreneurship involves:
- Active business management.
- Interaction with government agencies.
- Submission of reports and possible need for record keeping.
All these points require not just time, but also the personal attention of the entrepreneur or financial costs if he decides to entrust these responsibilities to his trusted person. An employed person must adequately assess his own strengths.
Examples of business restrictions
In the first section of this article, we looked at the obstacles that arise on the path of a future entrepreneur in the form of government restrictions. These obstacles are quite serious and significant, and they can only be circumvented legally in order to save personal funds and avoid prosecution.
Thus, the first obstacle is recognized as incapacity. This decision is made by a court hearing regarding a person held accountable for violating the law due to addictions. Thus, a drug addict who has been involved in theft may be declared incompetent, and similar cases. He will be able to open a business only after he is completely cured and his incapacity is refuted by the court itself.
Lawyers and notaries actually do not have the right to create individual entrepreneurs, just like deputies of the State Duma. Another thing is government officials.
Thus, a person who works as a teacher in a school cannot be recognized as a civil servant, therefore he retains the right to create his own business, but those people who work in the municipality of the Ministry of Education will be disappointed if they want to open an individual entrepreneur.
So, there is an opportunity to open an individual entrepreneur if you are officially employed, but not every person has it. Thus, employment in commercial organizations will not have any impact on the development of private business, but holding a public position becomes a basis for refusal to open an individual entrepreneur.
Is it possible to register an individual entrepreneur if you officially work?
Today in our country, few citizens work under an employment contract in only one job.
The desire to earn more money encourages a person to look for additional income and do something else besides his main job.
Some people get additional income from time to time, and some people make it even more than their main job. It is at this time that the desire to formalize your activities legally arises.
Beginning entrepreneurs often wonder whether it is possible to open an individual entrepreneur while working officially? According to the law, no one prohibits you from registering a company.
Of course, this has its own nuances, and it is worth initially understanding who is prohibited from conducting commercial activities and working at the same time.
It is also worth knowing when registration of an individual entrepreneur is mandatory and whether your activities will affect labor relations.
What does the law say?
In order to find out who is allowed and who is prohibited from engaging in individual entrepreneurship in our country, you need to read Article 18 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The article states that capable citizens of the Russian Federation over 18 years of age who have no restrictions on doing business can register an individual entrepreneur.
Even if you are under eighteen years old, you can register your individual entrepreneur, provided that your parents sign a written consent to this. Article 23 of the same Civil Code states that a citizen can conduct business activities from the moment of registering his enterprise with the local tax authority.
The article does not say that persons who are officially employed cannot organize their own individual entrepreneurs. Since an individual entrepreneur is not an LLC or OJSC, it is not an organizational and legal form.
An individual entrepreneur is an individual, therefore, he has the same rights and the opportunity to officially work, regardless of whether there is commercial activity or not. Of course, there are also prohibitions. For example, it is impossible to open an individual entrepreneur within 12 months after an individual is declared bankrupt by the Arbitration Court.
Also, those whose activities are related to public service will not be able to register. In this situation, civil servants should not be confused with employees of budgetary organizations.
Who cannot register an individual entrepreneur while working officially
As mentioned above, not all individuals who officially work can open their own private enterprise. The restrictions here apply to those people who are in the service of the state:
- deputies and officials;
- military personnel;
- police officers;
- heads of municipal enterprises.
There is also no opportunity for a notary or lawyer to become an individual entrepreneur. These restrictions are mainly due to the fact that people working for the state or representing the interests of the country are very busy. Commercial activity takes a lot of time, you need to do business constantly.
That is why, if civil servants engage in business, when will they do their work? Often, a person working in a state enterprise thinks that he is a civil servant. In government organizations there is a separation of civil servants and hired workers.
Also, positions assuming the status of civil servants are prescribed in the Presidential Decree.
To avoid problems and disagreements in the future, it’s a good idea to approach your manager and ask if it’s possible for you to open an individual entrepreneur at the same time as your official job? For example, a teacher at a municipal educational institution has the full right to carry out tutoring activities, but the head physician of a municipal hospital cannot conduct commercial activities. In any case, if you have doubts whether you are allowed to open your own business and continue working, it is better to consult with specialists or your immediate supervisor.
Combining entrepreneurial activity with main job
If, while working at an official job, you began to understand that entrepreneurial activity is your calling, you need to weigh the pros and cons. If at the beginning of your journey you decided to combine work and business, you should know that you have no obstacles.
It is necessary to plan everything, calculate the time, because entrepreneurship takes a lot of time, and your bosses at work will obviously not like the fact that you have become worse at your job. It is also worth calculating whether the business will live up to its expectations.
Of course, it is possible to do business and work at the same time, but you should know that this is also a costly business in terms of time and money. For example, contributions to the Pension Fund and Social Insurance Fund in 2017 amount to 27,990 rubles.
In any case, in order to open your own business, according to the laws of our state, it must first be registered. The process of registering an individual entrepreneur is the same for everyone, both for working citizens and for the unemployed. Registration of an enterprise takes place with the federal tax service at the place of registration of the individual. To begin registration, you need to collect a package of documents:
- Identity document. Passport of a Citizen of the Russian Federation (copies of its pages are also required).
- Taxpayer identification number, TIN (if you have not received a TIN, then upon successful registration, the tax service will automatically assign you this number).
- Application for registration in form P21001.
- Receipt for payment of the state fee for registering an enterprise (in 2018, the payment amount is 800 rubles; it is worth noting that if registration is refused, these funds are not returned).
It is also advisable to understand the enterprise taxation system before submitting these documents. In our country there are several forms of taxation, so it is better to choose a more suitable form in advance.
If you know in advance what form you will use to pay taxes to the state, together with a package of documents you submit a corresponding application to the tax service in two copies.
After three working days, you receive documents from the tax authority that confirm your status as an individual entrepreneur. From this moment you can start running your business legally. Remember that from this moment you also assume a number of legal obligations as a business entity, namely:
- keep a book of income and expenses;
- payment of taxes according to the chosen taxation system;
- making contributions to the Pension Fund and Social Insurance Fund.
Labor relations with the employer
From the point of view of the law, after you have registered with the tax service as an individual entrepreneur, there should be no problems with your employer. It is worth noting that there is no need to talk about the new status to everyone, and according to the law, there is no need to notify the manager that you are engaged in entrepreneurial activity.
From a legal point of view, everything looks good, but in practice there are often cases when the manager is not happy that his employee has started doing business.
Dissatisfaction may be due to the fact that the employee has begun to give less of his best at his workplace, and he devotes all his dedication and energy to his enterprise.
There are also situations when an employer wishes to reconsider its relationship with an employee. The bottom line is that if any work is performed by an individual entrepreneur and not an employee of the enterprise, the employer will save enough money that he would have to pay for you to the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund.
Also, your boss will not have to pay you for vacation or sick leave, or any other social packages. At first glance, this may seem like a big disadvantage for an individual entrepreneur, but in such a situation your tax to the state will be less.
Since for a hired worker it is 13% of wages, and an individual entrepreneur, when choosing a simplified taxation system, will pay only 6%.
Conclusion
Most people who run a business today, no matter how small or big, in most cases started small. Most entrepreneurs did not leave their jobs until they were convinced that the business was generating good income, which significantly exceeded wages.
The most important thing is that there are no regulations or laws that can prohibit you from doing business. If you do not belong to the category of citizens who have the status of civil servants, all roads are open to you. The main thing is that you can combine both activities, manage to work and run your organization.
After all, you cannot be an entrepreneur in your free time; you need to spend a lot of time and effort.
In another case, if you opened your own individual entrepreneur while unemployed, but over time you realize that you cannot provide for yourself because you lack experience, you can easily get an official job and combine business with work.
The work book does not contain information about entrepreneurial activity, so getting a job will not be difficult. Another thing is if you want to get a government job, then the individual entrepreneur will have to be closed.
It is worth remembering that opening an individual entrepreneur and working at the same time is not so important, the important thing is whether a person can cope with the responsibilities assigned to himself. In any case, everything depends on the individual, the main thing is to believe that everything will work out.
Does an employed person need to register an individual entrepreneur and do they need a license for installation work?
Can I open an individual entrepreneur if I work officially? What license is needed to carry out installation work?
Before registering as an individual entrepreneur, decide on the type of activity according to OKVED. You will need to indicate the selected type of activity in the application for individual entrepreneur registration. Then, depending on the type of activity, you will then choose the taxation system for individual entrepreneurs that you will apply.
The following OKVED code is suitable for installation work:
Code 43.2 Production of electrical, sanitary and other construction and installation works. This group includes: installation work that ensures the functioning of buildings and civil engineering structures, including the installation of electrical systems, plumbing and sewerage networks, gas supply networks, heating and air conditioning systems, elevators, etc.
Code 43.2 OKVED 2 is included in the following branch of the classifier of types of economic activities (decoding of higher codes):
- F - Section "Construction".
- 43 - Class “Specialized construction work.”
- 43.2 - Subclass “Production of electrical, sanitary and other construction and installation works.”
A complete list and breakdown of OKVED group codes included in this subclass:
- OKVED code 43.21 - Electrical installation work
- OKVED code 43.22 - Sanitary work, installation of heating systems and air conditioning systems
- OKVED code 43.29 - Production of other construction and installation works
When specifying the OKVED code, you must write down the four-digit value of the code and select the main type of activity. The main type of activity is considered to be one whose income will be at least 60% of total income. You can record up to 50 activities.
Activities for installation, maintenance and repair of fire safety equipment for buildings and structures were previously subject to licensing. Currently, instead of licenses, it is necessary to obtain permission for installation work.
The point is that companies that previously received licenses must now unite to obtain the status of self-regulatory organizations.
As a result, from January 1, 2010, any organization can, in one way or another, carry out its activities only if it has joined an SRO and received the appropriate SRO permits.
Individual entrepreneurs, as well as legal entities who wish to begin performing many construction, design, survey or energy audit work, are required to join any self-regulatory organization in their chosen specialization. You can find out whether an individual entrepreneur needs an SRO in the list published in Order 624 of the Ministry of Regional Development.
According to the Urban Planning Code, individual entrepreneurs who meet the requirements for issuing a certificate of admission to one or more types of work that affect the level of safety of buildings in capital construction are accepted into the self-regulatory organization. In this case, an individual entrepreneur can receive an SRO permit as a result of a positive decision on its issuance by the general meeting of participants in a self-regulatory partnership.
Each partnership establishes individual requirements for length of service, education, and the specialty of the entrepreneur and his hired workers (if any). Among the most common requirements for an entrepreneur to join an SRO are:
o The entrepreneur has a technical specialized education and work experience of at least three to five years. o The individual has a document on advanced training and certification (carried out at least once every five years).
o Relevant education, work experience and qualifications for each employee performing regulated activities.
To become a participant in a non-profit partnership, you must submit the following documents: SRO approval for individual entrepreneurs:
1. Completed application for admission to the partnership. It must indicate the types of work (that you plan to perform) that are available in Order 624 of the Ministry of the Region, registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on August 9, 2010 N 18086.
2. A copy of the document on registration in the state register of entrepreneurs.
3. Papers indicating the entrepreneur’s compliance with the requirements for issuing a certificate for the required types of work that affect the degree of safety of capital construction buildings.
4. Copies of approvals and certificates obtained from other self-regulatory organizations or certification centers (if they were issued).
Today, companies that do not have SRO permits are allowed to construct such facilities as:
- Residential buildings for a single family with no more than three storeys;
- Residential buildings with no more than three storeys, consisting of no more than ten block sections for each family, having a common wall with neighboring sections, and the house must be located on its own site and have a separate exit to public territory;
- Multi-apartment residential buildings with no more than three storeys, having in their design no more than four block sections. In the common areas of such houses there are several apartments with a separate entrance and access to public territory.
Conclusion:
You can carry out installation services in the above-mentioned facilities without a license and without SRO approval.
Detailed motivation for the conclusion:
Based on clause 6.1. Art. 18 Federal Law of 08.08.
2001 N 128-FZ “On licensing of certain types of activities”, licensing of design, construction and engineering surveys for the construction of buildings and structures ceased on January 1, 2010.
The current Federal Law of May 4, 2011 N 99-FZ “On licensing of certain types of activities” does not provide for licensing of construction activities.
From this date, construction activities are regulated exclusively by the norms of the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter - the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) and documents adopted in accordance with it.
Based on Part 2 of Art. 47, part 4 art. 48 and part 2 of Art.
52 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, types of work on engineering surveys, preparation of design documentation, as well as on construction, reconstruction and major repairs of capital construction projects that affect the safety of capital construction projects must be carried out only by individual entrepreneurs or legal entities that have certificates issued by a self-regulating organization about admission to such types of work. Other types of work on engineering surveys, design, construction, reconstruction, major repairs of capital construction projects can be performed by any individuals or legal entities.
In accordance with Part 4 of Art. 55.8 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, by order of the Ministry of Regional Development of Russia dated December 30, 2009 N 624, the List of types of work on engineering surveys, on the preparation of design documentation, on construction, reconstruction, and major repairs of capital construction projects that affect the safety of capital construction projects (hereinafter referred to as the List) was approved.
Paragraph 2 of this order establishes that the List does not include types of work on the preparation of project documentation, construction, reconstruction, major repairs in relation to objects for which the issuance of a construction permit is not required in accordance with paragraphs 1–4, 5, part 17 Art.
51 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, as well as in relation to individual housing construction projects (detached residential buildings with no more than three floors, intended for residence of no more than two families); residential buildings with no more than three floors, consisting of several blocks, the number of which does not exceed ten and each of which is intended for one family, has a common wall (common walls) without openings with the neighboring block or neighboring blocks, is located on a separate land plot and has access to public territory; apartment buildings with no more than three floors, consisting of one or more block sections, the number of which does not exceed four, each of which contains several apartments and common areas and each of which has a separate entrance with access to the common area.
Thus, at present, for the construction or repair of an individual residential building, cottage, or summer house, which has no more than three floors and is intended for residence of one or two families, an individual entrepreneur does not require a license or certificate of permission to work. The above also applies to the construction of “secondary” objects on a garden (dacha) plot of land: a garage, a canopy, a gazebo, a bathhouse, outbuildings, etc.
Is it possible to open an individual entrepreneur if you are officially employed - requirements and restrictions
The official definition of individual entrepreneurs (Article 11, Part 1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) states that individual entrepreneurs are individuals. It turns out that an individual entrepreneur, as an individual, has the right to work under an employment contract.
Regulatory background
According to the current legislation, it is possible to conduct business activities without forming a legal entity - for this you need to undergo state registration and obtain the status of an individual entrepreneur (see clause 1, article 23, chapter 3 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). And you can obtain this status even while working under the terms of an employment contract in any organization.
Existing restrictions
The above does not apply to some groups of people. Among them:
- Deputies of all levels, heads of municipalities and other persons holding elected positions.
- Notaries who are engaged in private practice, lawyers who have established law offices, as well as other forms of legal entities.
- Persons who do not have Russian citizenship or permission to carry out labor activities on the territory of the Russian Federation from the FMS.
Deputies, notaries and persons who do not have Russian citizenship will not be able to obtain the coveted certificate of registration of individual entrepreneurs.
Registration procedure
Even if you are already employed, the procedure for obtaining individual entrepreneur status will not differ from the standard one for you. It is quite simple and short-term, the main thing is to provide all the necessary documents to the Federal Tax Service inspection:
- application for state registration of an individual as an individual entrepreneur (form No. P21001);
- copy of Russian passport;
- receipt of payment of state duty in the amount of 800 rubles.
Carefully fill out the Application and prepare the documents provided, and then within 3 days you will receive a USRIP registration sheet.
To date, more than 5 million legal entities are registered in the Unified Register of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises of the Russian Federation, most of which are individual entrepreneurs (more than 3.8 million people as of 08/01/2017 according to the Federal Tax Service website).
The approved instructions for obtaining individual entrepreneur status are presented on the official website of the Federal Tax Service.
To register an individual business, you now need a minimum package of documents and several thousand rubles to pay for priority expenses
Features of paying taxes and insurance premiums
Having registered as an individual entrepreneur, you are required to pay your own insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of Russia and the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund. In addition, an individual entrepreneur can make social insurance contributions for further payments for sick leave and maternity leave, but on his own initiative - these payments are optional.
According to the employment contract, the company also pays insurance premiums for you to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation and the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund, but this fact does not relieve you of the obligation to pay “entrepreneurial” contributions. All these payments will be credited to your account and subsequently taken into account when forming your pension.
The activities of individual entrepreneurs also include the payment of taxes to the budget. There are two tax regimes; for small businesses, the most convenient will be a special tax regime that provides for a simplified taxation system. According to this system, the tax percentage is 6% on the amount of income or 15% on the amount of income reduced by the amount of expenses incurred.
You can learn more about the methods for calculating taxes for individual entrepreneurs on the official website of the Federal Tax Service.
Choosing a tax regime is an important step for any individual entrepreneur, so at this stage it makes sense to get advice from specialists from the Federal Tax Service.
Impact on relationships with superiors
According to the agreement concluded with the official employer, you are not required to report your status as an individual entrepreneur. This is not recorded in the work book. Therefore, except for an official request to the state register, the employer will not receive information about your status as an individual entrepreneur.
If the company's policy does not limit the employment of persons with individual entrepreneur status, many employers will not be against hiring you. Performing a work function as an individual entrepreneur reduces the tax base and social package for the employer - as an individual entrepreneur, you are obliged to pay for all this yourself.
The lower amount of taxes compensates for the lack of social benefits, vacation pay and sick leave payments provided for in the employment contract. If this option seems attractive to you, then consider switching to a civil contract with your employer.
However, such an agreement must be drawn up especially competently in order to avoid conflicts with the tax authorities: sometimes the transition from an employment to a civil law contract is considered as a deliberate measure to reduce the tax base. When drawing up a GPC Agreement between you and your employer, pay attention to the following:
- A civil contract provides only the following names of the parties: Customer and Contractor, and the name of the position is available only in the employment contract.
- Payment to the Contractor is made according to the amount of work performed and does not depend on the cost of an hour of work or salary.
- The GPC agreement should not contain any mention of the social package and working conditions for the Contractor.
- The Contractor is not obliged to comply with the internal labor regulations of the Customer’s company.
All of the above is provided only by an employment contract, which means that it may be considered by the tax service as a deliberate desire to pass off the employment relationship as a civil law relationship.
Maintain a good relationship with your superiors
If you understand that combining work and business activities will be within your capabilities, there is no need to sever ties with your official employer to obtain individual entrepreneur status. There will be no difficulties when registering, paying taxes and insurance premiums - all these procedures are standard.
How your individual entrepreneur status will affect your relationship with your superiors depends on the policy of the company where you are officially employed. If the company has no restrictions on hiring persons with the status of an individual entrepreneur, then you have no obstacles to combining official work and your own business.
Individual entrepreneur (IP)(obsolete private entrepreneur (PE), PBOYUL until 2005) is an individual registered as an entrepreneur without forming a legal entity, but in fact possessing many of the rights of legal entities. The rules of the civil code regulating the activities of legal entities apply to individual entrepreneurs, except in cases where separate articles of laws or legal acts are prescribed for entrepreneurs.()
Due to some legal restrictions (it is impossible to appoint full-fledged directors to branches in the first place), an individual entrepreneur is almost always a micro-business or small business.
according to the Code of Administrative Offenses
Fine from 500 to 2000 rubles
In case of gross violations or when working without a license - up to 8,000 rubles. And, it is possible to suspend activities for up to 90 days.
From RUB 0.9 million for three years, and the amount of arrears exceeds 10 percent of the tax payable;
From 2.7 million rubles.
Fine from 100 thousand to 300 thousand rubles. or in the amount of the culprit’s salary for 1-2 years;
Forced labor for up to 2 years);
Arrest for up to 6 months;
Imprisonment for up to 1 year
If the individual entrepreneur fully pays the amounts of arrears (taxes) and penalties, as well as the amount of the fine, then he is exempt from criminal prosecution (but only if this is his first such charge) (Article 198, paragraph 3 of the Criminal Code)
Evasion of taxes (fees) on an especially large scale (Article 198, paragraph 2. (b) of the Criminal Code)
From 4.5 million rubles. for three years, and the amount of arrears exceeds 20 percent of the tax payable;
From 30.5 million rubles.
Fine from 200 thousand to 500 thousand rubles. or in the amount of the culprit’s salary for 1.5-3 years;
Forced labor for up to 3 years;
Imprisonment for up to 3 years
Fine
If the amounts for criminal prosecution are not reached, then there will only be a fine.
Non-payment or incomplete payment of taxes (fees)
1. Non-payment or incomplete payment of tax (fee) amounts as a result of understatement of the tax base, other incorrect calculation of tax (fee) or other unlawful actions (inaction) entails a fine in the amount of 20 percent of the unpaid amount of tax (fee).
3. The acts provided for in paragraph 1 of this article, committed intentionally, entail a fine in the amount of 40 percent of the unpaid amount of tax (fee). (Article 122 of the Tax Code)
Penalty
If you were just late in payment (but did not provide false information), then there will be penalties.
The penalties for everyone are the same (1/300 multiplied by the key rate of the Central Bank per day of the amount of non-payment) and now amount to about 10% per annum (which is not very much in my opinion, taking into account the fact that banks give loans for at least 17-20 %). You can count them.
Licenses
Some types of activities an individual entrepreneur can only engage in after receiving a license, or permissions. Licensed activities of individual entrepreneurs include: pharmaceutical, private investigation, transportation of goods and passengers by rail, sea, air, as well as others.
An individual entrepreneur cannot engage in closed types of activities. These types of activities include the development and/or sale of military products, trafficking in narcotic drugs, poisons, etc. Since 2006, the production and sale of alcoholic beverages has also been prohibited. An individual entrepreneur cannot engage in: production of alcohol, wholesale and retail trade in alcohol (with the exception of beer and beer-containing products); insurance (i.e. be an insurer); activities of banks, investment funds, non-state pension funds and pawnshops; tour operator activities (travel agency is possible); production and repair of aviation and military equipment, ammunition, pyrotechnics; production of medicines (sales possible) and some others.
Differences from legal entities
- The state fee for registering individual entrepreneurs is 5 times less. In general, the registration procedure is much simpler and fewer documents are required.
- An individual entrepreneur does not require a charter and authorized capital, but he is liable for his obligations with all his property.
- An entrepreneur is not an organization. It is impossible for an individual entrepreneur to appoint a full and responsible director.
- Individual entrepreneurs do not have cash discipline and can manage the funds in the account as they please. Also, the entrepreneur makes business decisions without recording them. This does not apply to working with cash registers and BSO.
- An individual entrepreneur registers a business only in his name, in contrast to legal entities, where registration of two or more founders is possible. Individual entrepreneurship cannot be sold or re-registered.
- A hired employee of an individual entrepreneur has fewer rights than a hired employee of an organization. And although the Labor Code equates organizations and entrepreneurs in almost all respects, there are still exceptions. For example, when an organization is liquidated, the mercenary is required to pay compensation. When closing an individual entrepreneur, such an obligation exists only if it is specified in the employment contract.
Appointment of director
It is legally impossible to appoint a director in an individual entrepreneur. The individual entrepreneur will always be the main manager. However, you can issue a power of attorney to conclude transactions (clause 1 of Article 182 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Since July 1, 2014, it has been legislatively established for individual entrepreneurs to transfer the right to sign an invoice to third parties. Declarations could always be submitted through representatives.
All this, however, does not make the people to whom certain powers are delegated directors. A large legislative framework on rights and responsibilities has been developed for directors of organizations. In the case of an individual entrepreneur, one way or another, he himself is responsible under the contract, and with all his property he himself is responsible for any other actions of third parties by proxy. Therefore, issuing such powers of attorney is risky.
Registration
State registration of an individual entrepreneur carried out by the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation. The entrepreneur is registered with the district tax office at the place of registration, in Moscow - MI Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation No. 46 for Moscow.
Individual entrepreneurs can be
- adult, capable citizens of the Russian Federation
- minor citizens of the Russian Federation (from 16 years of age, with the consent of parents, guardians; married; a court or guardianship authority has made a decision on legal capacity)
- foreign citizens living in the Russian Federation
OKVED codes for individual entrepreneurs are the same as for legal entities
Necessary documents for registration of an individual entrepreneur:
- Application for state registration of an individual entrepreneur (1 copy). Sheet B of form P21001 must be filled out by the tax office and given to you.
- A copy of the Taxpayer Identification Number.
- A copy of your passport with registration on one page.
- Receipt for payment of the state fee for registration of an individual entrepreneur (800 rubles).
- Application for switching to the simplified tax system (If you need to switch).
An application for registration of individual entrepreneurs and other documents can be prepared online in a free service.
Within 5 days you will be registered as an individual entrepreneur or you will receive a refusal.
You must be given the following documents:
1) Certificate of state registration of an individual as an individual entrepreneur (OGRN IP)
2) Extract from the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs (USRIP)
After registration
After registering an individual entrepreneur It is necessary to register with the pension fund and the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund and obtain statistics codes.
Also necessary, but optional for an entrepreneur, is opening a current account, making a seal, registering a cash register, and registering with Rospotrebnadzor.
Taxes

Individual entrepreneur pays a fixed payment to the pension fund for the year, 2019 - 36,238 rubles + 1% of income over 300,000 rubles, 2018 - 32,385 rubles + 1% of income over 300,000 rubles. The fixed contribution is paid regardless of income, even if the income is zero. To calculate the amount, use the IP fixed payment calculator. There are also KBK and calculation details.
An individual entrepreneur can apply tax schemes: simplified tax system (simplified), UTII (imputed tax) or PSN (patent). The first three are called special modes and are used in 90% of cases, because they are preferential and simpler. The transition to any regime occurs voluntarily, upon application; if you do not write applications, then OSNO (general taxation system) will remain by default.
Taxation of an individual entrepreneur almost the same as for legal entities, but instead of income tax, personal income tax is paid (under OSNO). Another difference is that only entrepreneurs can use PSN. Also, individual entrepreneurs do not pay 13% on personal profits in the form of dividends.
An entrepreneur has never been obliged to keep accounting records (chart of accounts, etc.) and submit financial statements (this only includes a balance sheet and a financial performance statement). This does not exclude the obligation to keep tax records: declarations of the simplified tax system, 3-NDFL, UTII, KUDIR, etc.
An application for the simplified tax system and other documents can be prepared online in a free service.
Inexpensive programs for individual entrepreneurs include those with the ability to submit reports via the Internet. 500 rubles/month. Its main advantage is ease of use and automation of all processes.
Help
Credit
It is more difficult for an individual entrepreneur to get a loan from a bank than for a legal entity. Many banks also give mortgages with difficulty or require guarantors.
- An individual entrepreneur does not keep accounting records and it is more difficult for him to prove his financial solvency. Yes, there is tax accounting, but profit is not allocated there. Patent and UTII are especially opaque in this matter; these systems do not even record income. The simplified tax system “Income” is also unclear, because it is not clear how many expenses there are. The simplified tax system "Income-Expenditures", Unified Agricultural Tax and OSNO most clearly reflect the real state of the individual entrepreneur's business (there is an accounting of income and expenses), but unfortunately these systems are used less frequently.
- The individual entrepreneur himself (as opposed to the organization) cannot act as collateral in the bank. After all, he is an individual. The property of an individual can be collateral, but this is legally more complicated than collateral from an organization.
- An entrepreneur is one person - a person. When issuing a loan, the bank must take into account that this person can get sick, leave, die, get tired and decide to live in the country, giving up everything, etc. And if in an organization you can change the director and founders with the click of a finger, then in this case an individual entrepreneur can just close it and terminate the loan agreement or go to court. IP cannot be re-registered.
If a business loan is denied, then you can try to take out a consumer loan as an individual, without even disclosing your plans to spend money. Personal loans usually have high rates, but not always. Especially if the client can provide collateral or has a salary card with this bank.
Subsidy and support
In our country, hundreds of foundations (state and not only) provide consultations, subsidies, and preferential loans for individual entrepreneurs. Different regions have different programs and help centers (you need to search). .
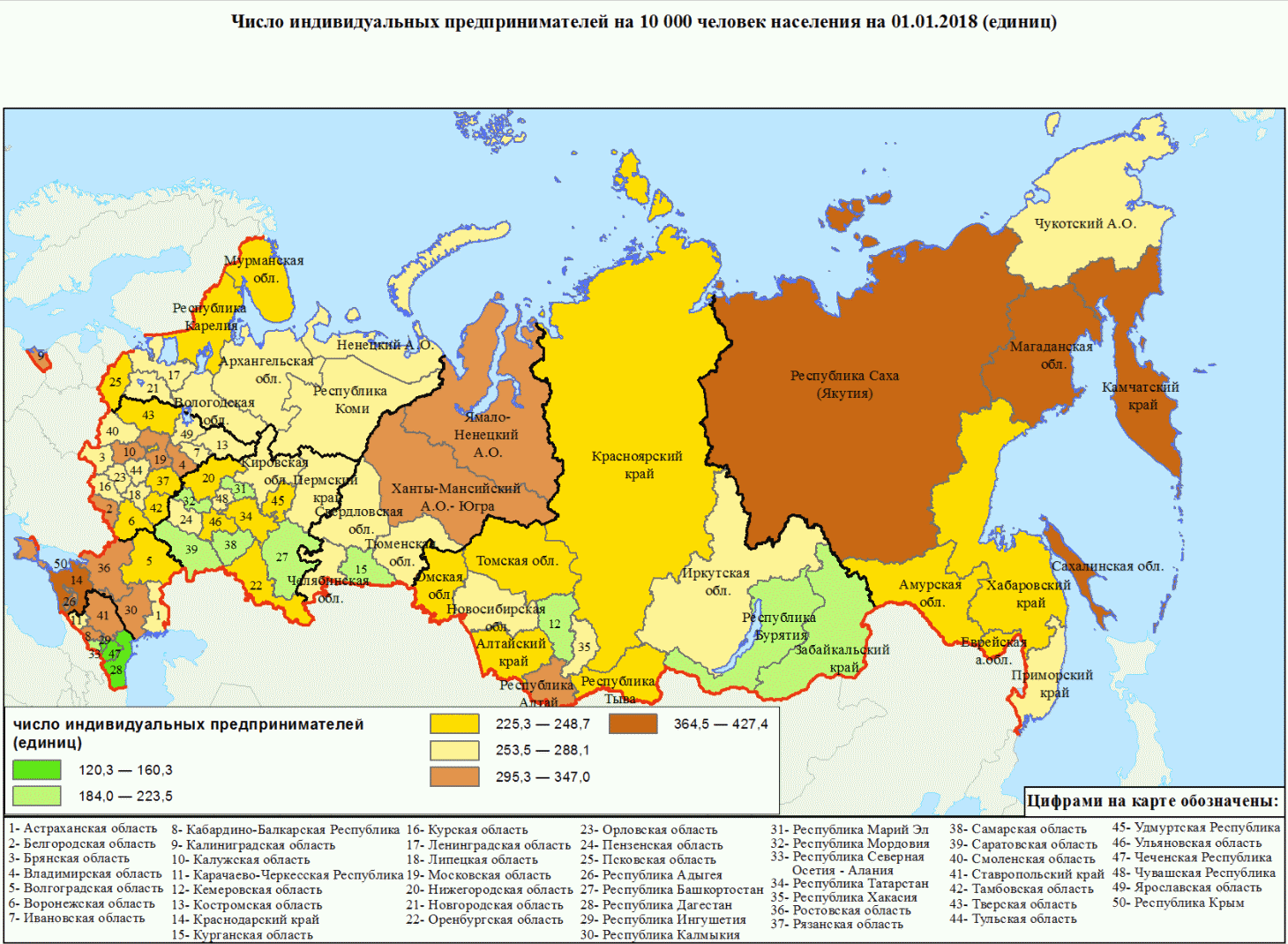

Rice. Number of individual entrepreneurs per 10,000 population
Experience
Pension experience
If the entrepreneur pays everything regularly to the Pension Fund, then the pension period runs from the moment of state registration until the closure of the individual entrepreneur, regardless of income.
Pension
According to current legislation, an individual entrepreneur will receive a minimum pension, regardless of how many contributions to the Pension Fund he pays.
The country is undergoing almost continuous pension reform and therefore it is not possible to accurately determine the size of the pension.
Since 2016, if a pensioner has the status of an individual entrepreneur, then his pension will not be indexed.
Insurance experience
The insurance period for the Social Insurance Fund only applies if the entrepreneur voluntarily pays contributions to the social insurance (FSS).
Difference from employees
The Labor Code does not apply to the individual entrepreneur himself. It is accepted only for hired workers. An individual entrepreneur, unlike a director, is not a mercenary.
Theoretically, an individual entrepreneur can hire himself, set a salary and make an entry in the work book. In this case, he will have all the rights of an employee. But it is not recommended to do this, because... then you will have to pay all salary taxes.
Only a female entrepreneur can receive maternity leave and only under the condition of voluntary social insurance. .
Any businessman, regardless of gender, can receive an allowance of up to one and a half. Either in RUSZN or in the FSS.
Individual entrepreneurs are not entitled to leave. Because he has no concept of working time or rest time and the production calendar also does not apply to him.
Sick leave is granted only to those who voluntarily insure themselves with the Social Insurance Fund. Calculated based on the minimum wage, the amount is insignificant, so in social insurance it makes sense only for mothers on maternity leave.
Closing
Liquidation of an individual entrepreneur is an incorrect term. An entrepreneur cannot be liquidated without violating the Criminal Code.
Closing an individual entrepreneur occurs in the following cases:
- in connection with the adoption of a decision by an individual entrepreneur to terminate activities;
- in connection with the death of a person registered as an individual entrepreneur;
- by court decision: forcibly
- in connection with the entry into force of a court verdict of deprivation of the right to engage in entrepreneurial activity;
- in connection with the cancellation of a document (overdue) confirming the right of this person to reside in Russia;
- in connection with a court decision to declare an individual entrepreneur insolvent (bankrupt).
Databases on all individual entrepreneurs
Website Contour.Focus
Partially free Contour.Focus The most convenient search. Just enter any number, last name, title. Only here you can find out OKPO and even accounting information. Some information is hidden.
Extract from the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs on the Federal Tax Service website
For free Federal Tax Service database Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs (OGRNIP, OKVED, Pension Fund number, etc.). Search by: OGRNIP/TIN or full name and region of residence (patronymic name does not have to be entered).
Bailiffs Service
For free FSSP Find out about enforcement proceedings for debt collection, etc.
With help, you can keep tax records on the simplified tax system and UTII, generate payment slips, 4-FSS, Unified Settlement, SZV-M, submit any reports via the Internet, etc. (from 325 rubles/month). 30 days free. Upon first payment. For newly created individual entrepreneurs now (free).
Question answer
Is it possible to register using temporary registration?
Registration is carried out at the address of permanent residence. To what is indicated in the passport. But you can send documents by mail. According to the law, it is possible to register an individual entrepreneur at the address of temporary registration at the place of stay, ONLY if there is no permanent registration in the passport (provided that it is more than six months old). You can conduct business in any city in the Russian Federation, regardless of the place of registration.
Can an individual entrepreneur register himself for work and make an entry in his employment record?
An entrepreneur is not considered an employee and does not make an entry in his employment record. Theoretically, he can apply for a job himself, but this is his personal decision. Then he must conclude an employment contract with himself, make an entry in the work book and pay deductions as for an employee. This is unprofitable and makes no sense.
Can an individual entrepreneur have a name?
An entrepreneur can choose any name for free that does not directly conflict with the registered one - for example, Adidas, Sberbank, etc. The documents and the sign on the door should still have the full name of the individual entrepreneur. He can also register the name (register a trademark): this costs more than 30 thousand rubles.
Is it possible to work?
Can. Moreover, you don’t have to tell them at work that you have your own business. This does not affect taxes and fees in any way. Taxes and fees to the Pension Fund must be paid - both as an individual entrepreneur and as a mercenary, in full.
Is it possible to register two individual entrepreneurs?
An individual entrepreneur is just the status of an individual. It is impossible to simultaneously become an individual entrepreneur twice (to obtain this status if you already have it). There is always one TIN.
What are the benefits?
There are no benefits in entrepreneurship for people with disabilities and other benefit categories.
Some commercial organizations also offer their own discounts and promotions. Online accounting Elba for newly created individual entrepreneurs is now free for the first year.





